Rational design of interleukin-21 antagonist through selective elimination of the gammaC binding epitope
- PMID: 20167599
- PMCID: PMC2852961
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.101444
Rational design of interleukin-21 antagonist through selective elimination of the gammaC binding epitope
Abstract
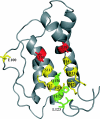
The cytokine interleukin (IL)-21 exerts pleiotropic effects acting through innate as well as adaptive immune responses. The activities of IL-21 are mediated through binding to its cognate receptor complex composed of the IL-21 receptor private chain (IL-21Ralpha) and the common gamma-chain (gammaC), the latter being shared by IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, and IL-15. The binding energy of the IL-21 ternary complex is predominantly provided by the high affinity interaction between IL-21 and IL-21Ralpha, whereas the interaction between IL-21 and gammaC, albeit essential for signaling, is rather weak. The design of IL-21 analogues, which have lost most or all affinity toward the signaling gammaC chain, while simultaneously maintaining a tight interaction with the private chain, would in theory represent candidates for IL-21 antagonists. We predicted the IL-21 residues, which compose the gammaC binding epitope using homology modeling and alignment with the related cytokines, IL-2 and IL-4. Next we systematically analyzed the predicted binding epitope by a mutagenesis study. Indeed two mutants, which have significantly impaired gammaC affinity with undiminished IL-21Ralpha affinity, were successfully identified. Functional studies confirmed that these two novel hIL-21 double mutants do act as hIL-21 antagonists.
Figures

References
-
- Spolski R., Leonard W. J. (2008) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 26, 57–79 - PubMed
-
- Nurieva R., Yang X. O., Martinez G., Zhang Y., Panopoulos A. D., Ma L., Schluns K., Tian Q., Watowich S. S., Jetten A. M., Dong C. (2007) Nature 448, 480–483 - PubMed
-
- Bondensgaard K., Breinholt J., Madsen D., Omkvist D. H., Kang L., Worsaae A., Becker P., Schiødt C. B., Hjorth S. A. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 23326–23336 - PubMed
-
- Asao H., Okuyama C., Kumaki S., Ishii N., Tsuchiya S., Foster D., Sugamura K. (2001) J. Immunol. 167, 1–5 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

