Parametric color coding of digital subtraction angiography
- PMID: 20167651
- PMCID: PMC7964185
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A2020
Parametric color coding of digital subtraction angiography
Abstract
Background and purpose: Color has been shown to facilitate both visual search and recognition tasks. It was our purpose to examine the impact of a color-coding algorithm on the interpretation of 2D-DSA acquisitions by experienced and inexperienced observers.
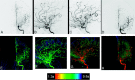
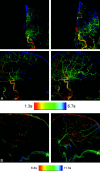
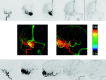
Materials and methods: Twenty-six 2D-DSA acquisitions obtained as part of routine clinical care from subjects with a variety of cerebrovascular disease processes were selected from an internal data base so as to include a variety of disease states (aneurysms, AVMs, fistulas, stenosis, occlusions, dissections, and tumors). Three experienced and 3 less experienced observers were each shown the acquisitions on a prerelease version of a commercially available double-monitor workstation (XWP, Siemens Healthcare). Acquisitions were presented first as a subtracted image series and then as a single composite color-coded image of the entire acquisition. Observers were then asked a series of questions designed to assess the value of the color-coded images for the following purposes: 1) to enhance their ability to make a diagnosis, 2) to have confidence in their diagnosis, 3) to plan a treatment, and 4) to judge the effect of a treatment. The results were analyzed by using 1-sample Wilcoxon tests.
Results: Color-coded images enhanced the ease of evaluating treatment success in >40% of cases (P < .0001). They also had a statistically significant impact on treatment planning, making planning easier in >20% of the cases (P = .0069). In >20% of the examples, color-coding made diagnosis and treatment planning easier for all readers (P < .0001). Color-coding also increased the confidence of diagnosis compared with the use of DSA alone (P = .056). The impact of this was greater for the naïve readers than for the expert readers.
Conclusions: At no additional cost in x-ray dose or contrast medium, color-coding of DSA enhanced the conspicuity of findings on DSA images. It was particularly useful in situations in which there was a complex flow pattern and in evaluation of pre- and posttreatment acquisitions. Its full potential remains to be defined.
Figures
Comment in
-
Color-coded digital subtraction angiography: the end of a monochromatic era?AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010 May;31(5):925-7. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2077. Epub 2010 Apr 15. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010. PMID: 20395396 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Parametric color coding of digital subtraction angiography in the evaluation of carotid cavernous fistulas.Clin Neuroradiol. 2013 Jun;23(2):113-20. doi: 10.1007/s00062-012-0184-8. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Clin Neuroradiol. 2013. PMID: 23241650
-
Color-coded digital subtraction angiography: the end of a monochromatic era?AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010 May;31(5):925-7. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2077. Epub 2010 Apr 15. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010. PMID: 20395396 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Bone marrow edema pattern identification in patients with lytic bone lesions using digital subtraction angiography-like bone subtraction on large-area detector computed tomography.Invest Radiol. 2014 Mar;49(3):156-64. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000007. Invest Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24220254 Clinical Trial.
-
A methodology for validating a 3D imaging modality for brain AVM delineation: application to 3DRA.Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2008 Oct;32(7):544-53. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2008.06.003. Epub 2008 Jul 18. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2008. PMID: 18640005
-
Improvement in C-arm acquired DSA image quality via combined effect of inverse consistent motion correction and nonlinear normalization.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2007;2007:876-9. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2007.4352430. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2007. PMID: 18002096
Cited by
-
In-room assessment of cerebral blood volume for guidance during intra-arterial thrombolytic therapy.Interv Neuroradiol. 2012 Dec;18(4):463-8. doi: 10.1177/159101991201800413. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Interv Neuroradiol. 2012. PMID: 23217642 Free PMC article.
-
A technique for intra-procedural blood velocity quantitation using time-resolved 2D digital subtraction angiography.CVIR Endovasc. 2021 Jan 7;4(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s42155-020-00199-y. CVIR Endovasc. 2021. PMID: 33411087 Free PMC article.
-
perfDSA: Automatic Perfusion Imaging in Cerebral Digital Subtraction Angiography.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2025 Jun;20(6):1195-1203. doi: 10.1007/s11548-025-03359-4. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2025. PMID: 40272658 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of ocular blood flow in the assessment of symptomatic carotid stenosis.Interv Neuroradiol. 2025 Aug;31(4):475-481. doi: 10.1177/15910199231169844. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Interv Neuroradiol. 2025. PMID: 37070150 Free PMC article.
-
Flow-diverting stents allow efficient treatment of unruptured, intradural dissecting aneurysms of the vertebral artery: An explanatory approach using in vivo flow analysis.Interv Neuroradiol. 2016 Feb;22(1):76-83. doi: 10.1177/1591019915609166. Epub 2015 Oct 29. Interv Neuroradiol. 2016. PMID: 26515700 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Cole BL, Maddocks JD, Sharpe K. Visual search and the conspicuity of coloured targets for colour vision normal and colour vision deficient observers. Clin Exp Optom 2004;87:294–304 - PubMed
-
- D'Zmura M. Color in visual search. Vision Res 1991;31:951–66 - PubMed
-
- Heintzen PH, Bürsch HJ, Hahne HJ, et al. . Assessment of cardiovascular function by digital angiocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol 1985:5:150S–57S - PubMed
-
- Cusma JT, Toggart EJ, Folts JD, et al. . Digital subtraction angiograpic imaging of coronary flow reserve. Circulation 1987;75:461–72 - PubMed
-
- Bürsch HJ. Funktionsangiokardiographie. Kardiologie 1989;78(suppl 7):181–86 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
