Identification of pathogens by mass spectrometry
- PMID: 20167691
- PMCID: PMC7108202
- DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2009.138867
Identification of pathogens by mass spectrometry
Abstract
Background: Mass spectrometry (MS) is a suitable technology for microorganism identification and characterization.
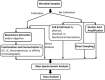
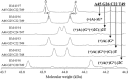
Content: This review summarizes the MS-based methods currently used for the analyses of pathogens. Direct analysis of whole pathogenic microbial cells using MS without sample fractionation reveals specific biomarkers for taxonomy and provides rapid and high-throughput capabilities. MS coupled with various chromatography- and affinity-based techniques simplifies the complexity of the signals of the microbial biomarkers and provides more accurate results. Affinity-based methods, including those employing nanotechnology, can be used to concentrate traces of target microorganisms from sample solutions and, thereby, improve detection limits. Approaches combining amplification of nucleic acid targets from pathogens with MS-based detection are alternatives to biomarker analyses. Many data analysis methods, including multivariate analysis and bioinformatics approaches, have been developed for microbial identification. The review concludes with some current clinical applications of MS in the identification and typing of infectious microorganisms, as well as some perspectives.
Summary: Advances in instrumentation (separation and mass analysis), ionization techniques, and biological methodologies will all enhance the capabilities of MS for the analysis of pathogens.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Advances in mass spectrometry for the identification of pathogens.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2011 Nov-Dec;30(6):1203-24. doi: 10.1002/mas.20320. Epub 2011 May 9. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2011. PMID: 21557290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry characterization of protein patterns, protein markers and whole proteomes for pathogenic bacteria.J Microbiol Methods. 2013 Mar;92(3):381-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2013.01.004. Epub 2013 Jan 12. J Microbiol Methods. 2013. PMID: 23318550 Review.
-
Proteotyping: Proteomic characterization, classification and identification of microorganisms--A prospectus.Syst Appl Microbiol. 2015 Jun;38(4):246-57. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25933927 Review.
-
Mass Spectrometry in Microbial Forensics.Forensic Sci Rev. 2009 Jan;21(1):25-50. Forensic Sci Rev. 2009. PMID: 26242239 Review.
-
Mass Spectrometry Techniques in Emerging Pathogens Studies: COVID-19 Perspectives.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2020 Oct 7;31(10):2013-2024. doi: 10.1021/jasms.0c00238. Epub 2020 Sep 16. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2020. PMID: 32880453 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid identification of Bacillus anthracis spores in suspicious powder samples by using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS).Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Sep;79(17):5372-83. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01724-13. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23811517 Free PMC article.
-
Laboratory diagnosis of tuberculosis in resource-poor countries: challenges and opportunities.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011 Apr;24(2):314-50. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00059-10. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21482728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluorescent DNA chemosensors: identification of bacterial species by their volatile metabolites.Chem Commun (Camb). 2011 Nov 7;47(41):11435-7. doi: 10.1039/c1cc14871k. Epub 2011 Sep 21. Chem Commun (Camb). 2011. PMID: 21935547 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplexing the Identification of Microorganisms via Tandem Mass Tag Labeling Augmented by Interference Removal through a Novel Modification of the Expectation Maximization Algorithm.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2024 Jun 5;35(6):1138-1155. doi: 10.1021/jasms.3c00445. Epub 2024 May 13. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2024. PMID: 38740383 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of bacteria in juice/lettuce using magnetic nanoparticles and selected reaction monitoring mass spectrometry.J Food Drug Anal. 2019 Apr;27(2):575-584. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2018.09.006. Epub 2018 Oct 26. J Food Drug Anal. 2019. PMID: 30987729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Demirev PA, Fenselau C. Mass spectrometry for rapid characterization of microorganisms. Annu Rev Anal Chem 2008;1:3.1-3.23. - PubMed
-
- Gu H, Ho P-L, Tsang KWT, Wang L, Xu B. Using biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles to capture vancomycin-resistant Enterococci and other gram-positive bacteria at ultralow concentration. J Am Chem Soc 2003;125:15702-15703. - PubMed
-
- Liu JC, Tsai PJ, Lee YC, Chen YC. Affinity capture of uropathogenic Escherichia coli using pigeon ovalbumin-bound Fe3O4@Al2O3 magnetic nanoparticles. Anal Chem 2008;80:5425-5432. - PubMed
-
- Afonso C, Fenselau C. Use of bioactive glass slides for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization analysis: application to microorganisms. Anal Chem 2003;75:694-697. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

