Acetylation of metabolic enzymes coordinates carbon source utilization and metabolic flux
- PMID: 20167787
- PMCID: PMC4183141
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1179687
Acetylation of metabolic enzymes coordinates carbon source utilization and metabolic flux
Erratum in
- Science. 2010 May 21;328(5981):974
Abstract
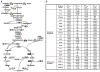
Lysine acetylation regulates many eukaryotic cellular processes, but its function in prokaryotes is largely unknown. We demonstrated that central metabolism enzymes in Salmonella were acetylated extensively and differentially in response to different carbon sources, concomitantly with changes in cell growth and metabolic flux. The relative activities of key enzymes controlling the direction of glycolysis versus gluconeogenesis and the branching between citrate cycle and glyoxylate bypass were all regulated by acetylation. This modulation is mainly controlled by a pair of lysine acetyltransferase and deacetylase, whose expressions are coordinated with growth status. Reversible acetylation of metabolic enzymes ensure that cells respond environmental changes via promptly sensing cellular energy status and flexibly altering reaction rates or directions. It represents a metabolic regulatory mechanism conserved from bacteria to mammals.
Figures

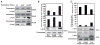

Comment in
-
Cell biology. Rise of the rival.Science. 2010 Feb 19;327(5968):964-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1187159. Science. 2010. PMID: 20167774 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

