The role of surfactant protein A in bleomycin-induced acute lung injury
- PMID: 20167853
- PMCID: PMC2894409
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200907-1002OC
The role of surfactant protein A in bleomycin-induced acute lung injury
Abstract
Rationale: Surfactant protein A (SP-A) is a collectin family member that has multiple immunomodulatory roles in lung host defense. SP-A levels are altered in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid and serum of patients with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome, suggesting the importance of SP-A in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury.
Objectives: Investigate the role of SP-A in the murine model of noninfectious lung injury induced by bleomycin treatment.
Methods: Wild-type (WT) or SP-A deficient (SP-A(-/-)) mice were challenged with bleomycin, and various indices of lung injury were analyzed.
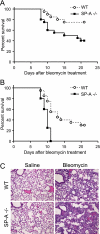
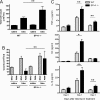
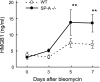
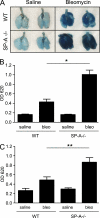
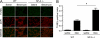
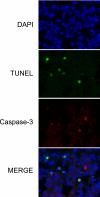
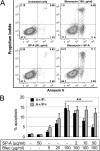
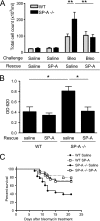
Measurements and main results: On challenge with bleomycin, SP-A(-/-) mice had a decreased survival rate as compared with WT mice. SP-A(-/-) mice had a higher degree of neutrophil-dominant cell recruitment and the expression of the inflammatory cytokines in BAL fluid than did WT mice. In addition, SP-A(-/-) mice had increased lung edema as assessed by the increased levels of intravenously injected Evans blue dye leaking into the lungs. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling and active caspase-3 staining suggested the increased apoptosis in the lung sections from SP-A(-/-) mice challenged with bleomycin. SP-A also specifically reduced bleomycin-induced apoptosis in mouse lung epithelial 12 cells in vitro. Moreover, intratracheal administration of exogenous SP-A rescued the phenotype of SP-A(-/-) mice in vivo.
Conclusions: These data suggest that SP-A plays important roles in modulating inflammation, apoptosis, and epithelial integrity in the lung in response to acute noninfectious challenges.
Figures
References
-
- Ashbaugh DG, Bigelow DB, Petty TL, Levine BE. Acute respiratory distress in adults. Lancet 1967;2:319–323. - PubMed
-
- Wheeler AP, Bernard GR. Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: a clinical review. Lancet 2007;369:1553–1564. - PubMed
-
- Wright JR. Immunoregulatory functions of surfactant proteins. Nat Rev Immunol 2005;5:58–68. - PubMed
-
- Borron P, McIntosh JC, Korfhagen TR, Whitsett JA, Taylor J, Wright JR. Surfactant-associated protein A inhibits LPS-induced cytokine and nitric oxide production in vivo. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2000;278:840–847. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

