Tumor suppressor function of androgen receptor coactivator ARA70alpha in prostate cancer
- PMID: 20167864
- PMCID: PMC2843478
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090293
Tumor suppressor function of androgen receptor coactivator ARA70alpha in prostate cancer
Abstract
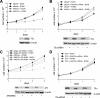
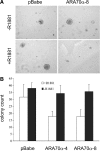
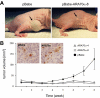
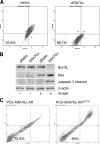
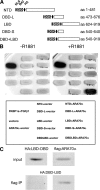
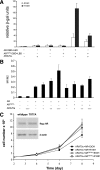
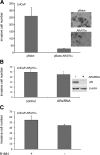
Androgen receptor (AR), a member of the steroid receptor family, is a transcription factor that has an important role in the regulation of both prostate cell proliferation and growth suppression. AR coactivators may influence the transition between cell growth and growth suppression. We have shown previously that the internally spliced ARA70 isoform, ARA70beta, promotes prostate cancer cell growth and invasion. Here we report that the full length ARA70alpha, in contrast, represses prostate cancer cell proliferation and anchorage-independent growth in vitro and inhibits tumor growth in nude mice xenograft experiments in vivo. Further, the growth inhibition by ARA70alpha is AR-dependent and mediated through induction of apoptosis rather than cell cycle arrest. Interestingly, AR with T877A mutation in LNCaP cells decreased its physical and functional interaction with ARA70alpha, facilitating the growth of LNCaP cells. The tumor suppressor function of ARA70alpha is consistent with our previous findings that ARA70alpha expression is decreased in prostate cancer cells compared with benign prostate. ARA70alpha also reduced the invasion ability of LNCaP cells. Although growth inhibition by ARA70alpha is AR-dependent, the inhibition of cell invasion is an androgen-independent process. These results strongly suggest that ARA70alpha functions as a tumor suppressor gene.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Androgen receptor coactivator ARA70alpha and ARA70beta isoform-specific antibodies: new tools for studies of expression and immunohistochemical localization.Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2008 Jan;16(1):7-12. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0b013e31802e91ea. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2008. PMID: 18091327
-
Distinct function of androgen receptor coactivator ARA70α and ARA70β in mammary gland development, and in breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Jul;128(2):391-400. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-1131-5. Epub 2010 Sep 3. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011. PMID: 20814820
-
Androgen receptor coactivators that inhibit prostate cancer growth.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2014 Apr 5;2(1):62-70. eCollection 2014. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2014. PMID: 25374906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stimulation of prostate cancer cellular proliferation and invasion by the androgen receptor co-activator ARA70.Am J Pathol. 2008 Jan;172(1):225-35. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070065. Epub 2007 Dec 21. Am J Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18156210 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and function of androgen receptor coactivators in prostate cancer.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2004 Nov;92(4):265-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2004.10.003. Epub 2004 Dec 19. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15663989 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression and function of nuclear receptor co-activator 4: evidence of a potential role independent of co-activator activity.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Dec;69(23):3895-909. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1000-y. Epub 2012 May 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22562579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Central role of RET in thyroid cancer.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Dec 1;5(12):a009233. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a009233. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 24296167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NCOA4-Mediated Ferritinophagy Is a Pancreatic Cancer Dependency via Maintenance of Iron Bioavailability for Iron-Sulfur Cluster Proteins.Cancer Discov. 2022 Sep 2;12(9):2180-2197. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-0043. Cancer Discov. 2022. PMID: 35771492 Free PMC article.
-
Imbalanced expression of Tif1γ inhibits pancreatic ductal epithelial cell growth.Am J Cancer Res. 2014 May 26;4(3):196-210. eCollection 2014. Am J Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24959375 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid Cancer: Role of RET and Beyond.Eur Thyroid J. 2012 Apr;1(1):15-23. doi: 10.1159/000336975. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Eur Thyroid J. 2012. PMID: 24782993 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brinkmann AO, Blok LJ, de Ruiter PE, Doesburg P, Steketee K, Berrevoets CA, Trapman J. Mechanisms of androgen receptor activation and function. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1999;69:307–313. - PubMed
-
- Chmelar R, Buchanan G, Need EF, Tilley W, Greenberg NM. Androgen receptor coregulators and their involvement in the development and progression of prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 2007;120:719–733. - PubMed
-
- Linja MJ, Porkka KP, Kang Z, Savinainen KJ, Janne OA, Tammela TL, Vessella RL, Palvimo JJ, Visakorpi T. Expression of androgen receptor coregulators in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:1032–1040. - PubMed
-
- Buchanan G, Irvine RA, Coetzee GA, Tilley WD. Contribution of the androgen receptor to prostate cancer predisposition and progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2001;20:207–223. - PubMed
-
- Culig Z, Bartsch G. Androgen axis in prostate cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2006;99:373–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

