Transcription factor Stat3 stimulates metastatic behavior of human prostate cancer cells in vivo, whereas Stat5b has a preferential role in the promotion of prostate cancer cell viability and tumor growth
- PMID: 20167868
- PMCID: PMC2843484
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090653
Transcription factor Stat3 stimulates metastatic behavior of human prostate cancer cells in vivo, whereas Stat5b has a preferential role in the promotion of prostate cancer cell viability and tumor growth
Abstract
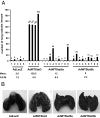
Identification of the molecular changes that promote viability and metastatic behavior of prostate cancer is critical for the development of improved therapeutic interventions. Stat5a/b and Stat3 are both constitutively active in locally-confined and advanced prostate cancer, and both transcription factors have been reported to be critical for the viability of prostate cancer cells. We recently showed that Stat3 promotes metastatic behavior of human prostate cancer cells not only in vitro but also in an in vivo experimental metastases model. In this work, we compare side-by-side Stat5a/b versus Stat3 in the promotion of prostate cancer cell viability, tumor growth, and induction of metastatic colonization in vivo. Inhibition of Stat5a/b induced massive death of prostate cancer cells in culture and reduced both subcutaneous and orthotopic prostate tumor growth, whereas Stat3 had a predominant role over Stat5a/b in promoting metastases formation of prostate cancer cells in vivo in nude mice. The molecular mechanisms underlying the differential biological effects induced by these two transcription factors involve largely different sets of genes regulated by Stat5a/b versus Stat3 in human prostate cancer model systems. Of the two Stat5 homologs, Stat5b was more important for supporting growth of prostate cancer cells than Stat5a. This work provides the first mechanistic comparison of the biological effects induced by transcription factors Stat5a/b versus Stat3 in prostate cancer.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Pharmacologic inhibition of Jak2-Stat5 signaling By Jak2 inhibitor AZD1480 potently suppresses growth of both primary and castrate-resistant prostate cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Oct 15;19(20):5658-74. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0422. Epub 2013 Aug 13. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23942095 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 promotes growth of human prostate cancer cells in vivo.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Mar 1;14(5):1317-24. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-2024. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18316550
-
Autocrine prolactin promotes prostate cancer cell growth via Janus kinase-2-signal transducer and activator of transcription-5a/b signaling pathway.Endocrinology. 2007 Jul;148(7):3089-101. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-1761. Epub 2007 Apr 5. Endocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17412813
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5a/b: biomarker and therapeutic target in prostate and breast cancer.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011 Oct;43(10):1417-21. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2011.06.007. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21704724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5A/B in prostate and breast cancers.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2008 Jun;15(2):367-90. doi: 10.1677/ERC-08-0013. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18508994 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
STAT5A/B gene locus undergoes amplification during human prostate cancer progression.Am J Pathol. 2013 Jun;182(6):2264-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.02.044. Epub 2013 May 7. Am J Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23660011 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated YKL40 is associated with advanced prostate cancer (PCa) and positively regulates invasion and migration of PCa cells.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014 Oct;21(5):723-37. doi: 10.1530/ERC-14-0267. Epub 2014 Jun 30. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24981110 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting Major Signaling Pathways throughout the Development of Prostate Cancer.Prostate Cancer. 2013;2013:920612. doi: 10.1155/2013/920612. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Prostate Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23738079 Free PMC article.
-
The tumor suppressor hTid1 inhibits STAT5b activity via functional interaction.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 18;286(7):5034-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.155903. Epub 2010 Nov 24. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21106534 Free PMC article.
-
17β-Estradiol and ICI182,780 Differentially Regulate STAT5 Isoforms in Female Mammary Epithelium, With Distinct Outcomes.J Endocr Soc. 2018 Feb 26;2(3):293-309. doi: 10.1210/js.2017-00399. eCollection 2018 Mar 1. J Endocr Soc. 2018. PMID: 29594259 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Damber JE, Aus G. Prostate cancer. Lancet. 2008;371:1710–1721. - PubMed
-
- Ahonen TJ, Xie J, LeBaron MJ, Zhu J, Nurmi M, Alanen K, Rui H, Nevalainen MT. Inhibition of transcription factor Stat5 induces cell death of human prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:27287–27292. - PubMed
-
- Li H, Zhang Y, Glass A, Zellweger T, Gehan E, Bubendorf L, Gelmann EP, Nevalainen MT. Activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-5 in prostate cancer predicts early recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:5863–5868. - PubMed
-
- Li H, Ahonen TJ, Alanen K, Xie J, LeBaron MJ, Pretlow TG, Ealley EL, Zhang Y, Nurmi M, Singh B, Martikainen PM, Nevalainen MT. Activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 in human prostate cancer is associated with high histological grade. Cancer Res. 2004;64:4774–4782. - PubMed
-
- Mora LB, Buettner R, Seigne J, Diaz J, Ahmad N, Garcia R, Bowman T, Falcone R, Fairclough R, Cantor A, Muro-Cacho C, Livingston S, Karras J, Pow-Sang J, Jove R. Constitutive activation of Stat3 in human prostate tumors and cell lines: direct inhibition of Stat3 signaling induces apoptosis of prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2002;62:6659–6666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

