Toll-like receptor 3 ligand dampens liver inflammation by stimulating Valpha 14 invariant natural killer T cells to negatively regulate gammadeltaT cells
- PMID: 20167870
- PMCID: PMC2843469
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090738
Toll-like receptor 3 ligand dampens liver inflammation by stimulating Valpha 14 invariant natural killer T cells to negatively regulate gammadeltaT cells
Abstract
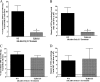
Valpha14 invariant natural killer T (Valpha14iNKT) cells are at the interface between the innate and adaptive immune responses and are thus critical for providing full engagement of host defense. We investigated the role of polyriboinosinic:polycytidylic acid (poly I:C), a replication-competent viral double-stranded RNA mimic and a specific agonist that recognizes the cellular sensor Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3), in regulating Valpha14iNKT cell activation. We established for the first time that hepatic Valpha14iNKT cells up-regulate TLR3 extracellularly after poly I:C treatment. Notably, activation of TLR3-expressing hepatic Valpha14iNKT cells by a TLR3 ligand was suppressed by TLR3 deficiency. Our studies also revealed that Valpha14iNKT cell activation in response to poly I:C administration uniquely suppressed the accumulation and activation of intrahepatic gammadeltaT cells (but not natural killer cells) by inducing apoptosis. Furthermore, we established that activated hepatic Valpha14iNKT cells (via cytokines and possibly reactive oxygen species) influenced the frequency and absolute number of intrahepatic gammadeltaT cells, as evidenced by increased hepatic gammadeltaT cell accumulation in Valpha14iNKT cell-deficient mice after poly I:C treatment relative to wild-type mice. Thus, hepatic Valpha14iNKT cells and intrahepatic gammadeltaT cells are functionally linked on application of TLR3 agonist. Overall, our results demonstrate a novel and previously unrecognized anti-inflammatory role for activated hepatic Valpha14iNKT cells in negatively regulating intrahepatic gammadeltaT cell accumulation (probably through TLR3 signaling) and thereby preventing potentially harmful activation of intrahepatic gammadeltaT cells.
Figures


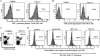
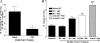


References
-
- Van Kaer L. α-Galactosylceramide therapy for autoimmune diseases: prospects and obstacles. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:31–42. - PubMed
-
- Kronenberg M. Toward an understanding of NKT cell biology: progress and paradoxes. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:877–900. - PubMed
-
- Wilson MT, Singh AK, Van Kaer L. Immunotherapy with ligands of natural killer T cells. Trends Mol Med. 2002;8:225–231. - PubMed
-
- Wilson MT, Van Kaer L. Natural killer T cells as targets for therapeutic intervention in autoimmune diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 2003;9:201–220. - PubMed
-
- Bendelac A, Savage PB, Teyton L. The biology of NKT cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:297–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

