Lifetime segmented assimilation trajectories and health outcomes in Latino and other community residents
- PMID: 20167890
- PMCID: PMC2836354
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2009.167999
Lifetime segmented assimilation trajectories and health outcomes in Latino and other community residents
Erratum in
- Am J Public Health. 2011 Jan;101(1):6
Abstract
Objectives: Under an ecodevelopmental framework, we examined lifetime segmented assimilation trajectories (diverging assimilation pathways influenced by prior life conditions) and related them to quality-of-life indicators in a diverse sample of 258 men in the Phoenix, AZ, metropolitan area.
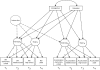
Methods: We used a growth mixture model analysis of lifetime changes in socioeconomic status, and used acculturation to identify distinct lifetime segmented assimilation trajectory groups, which we compared on life satisfaction, exercise, and dietary behaviors. We hypothesized that lifetime assimilation change toward mainstream American culture (upward assimilation) would be associated with favorable health outcomes, and downward assimilation change with unfavorable health outcomes.
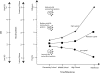
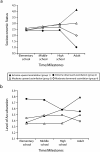
Results: A growth mixture model latent class analysis identified 4 distinct assimilation trajectory groups. In partial support of the study hypotheses, the extreme upward assimilation trajectory group (the most successful of the assimilation pathways) exhibited the highest life satisfaction and the lowest frequency of unhealthy food consumption.
Conclusions: Upward segmented assimilation is associated in adulthood with certain positive health outcomes. This may be the first study to model upward and downward lifetime segmented assimilation trajectories, and to associate these with life satisfaction, exercise, and dietary behaviors.
Figures
References
-
- Redfield R, Linton R, Herskovitz M. Memorandum for the study of acculturation. Am Anthropol 1936;38:149–152
-
- Berry JW. Conceptual approaches to acculturation. : Chun KM, Organista PB, Marin G, Acculturation: Advances in Theory, Measurement, and Applied Research Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; 2003:17–37
-
- Thomson MD, Hoffman-Goetz L. Defining and measuring acculturation: a systematic review of public health studies with Hispanic populations in the United States. Soc Sci Med 2009;69(7):983–991 - PubMed
-
- Cabassa LJ. Measuring acculturation: where we are and what we need to do. Hisp J Behav Sci 2003;25(2):127–146
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

