Tuberculosis transmission and use of methamphetamines in Snohomish County, WA, 1991-2006
- PMID: 20167896
- PMCID: PMC2978177
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2009.162388
Tuberculosis transmission and use of methamphetamines in Snohomish County, WA, 1991-2006
Abstract
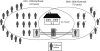
Objectives: We investigated a cluster of tuberculosis (TB) cases among persons using methamphetamines in Snohomish County, Washington, to determine the extent of the outbreak, examine whether methamphetamine use contributed to TB transmission, and implement strategies to prevent further infections.
Methods: We screened contacts to find and treat persons with TB disease or infection. We then formed a multidisciplinary team to engage substance abuse services partners and implement outreach strategies including novel methods for finding contacts and a system of incentives and enablers to promote finding, screening, and treating patients with TB and their infected contacts.
Results: We diagnosed and completed treatment with 10 persons with TB disease. Eight of 9 adult patients and 67% of their adult contacts reported using methamphetamines. Of the 372 contacts, 319 (85.8%) were screened, 80 (25.1%) were infected, 71 (88.8%) started treatment for latent infection, and 57 (80.3%) completed treatment for latent infection.
Conclusions: Collaborative approaches integrating TB control, outreach, incentives, and enablers resulted in high rates of treatment adherence and completion among patients and infected contacts. TB control programs should collaborate with substance abuse programs to address addiction, overcome substance abuse-related barriers to treatment, treat TB, and prevent ongoing transmission.
Figures
References
-
- Reichman LB, Felton CP, Edsall JR. Drug dependence, a possible new risk factor for tuberculosis disease. Arch Intern Med. 1979;139(3):337–339 - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Crack cocaine use among persons with tuberculosis—Contra Costa County, California, 1987–1990. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1991;40(29):485–489 - PubMed
-
- Kline SE, Hedemark LL, Davies SF. Outbreak of tuberculosis among regular patrons of a neighborhood bar. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(4):222–227 - PubMed
-
- Malakmadze N, Gonzalez IM, Oemig T, et al. Unsuspected recent transmission of tuberculosis among high-risk groups: implications of universal tuberculosis genotyping in its detection. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40(3):366–373 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

