Structural basis for the function of DEAH helicases
- PMID: 20168331
- PMCID: PMC2838688
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2010.11
Structural basis for the function of DEAH helicases
Abstract
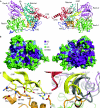
DEAH helicases participate in pre-messenger RNA splicing and ribosome biogenesis. The structure of yeast Prp43p-ADP reveals the homology of DEAH helicases to DNA helicases and the presence of an oligonucleotide-binding motif. A beta-hairpin from the second RecA domain is wedged between two carboxy-terminal domains and blocks access to the occluded RNA binding site formed by the RecA domains and a C-terminal domain. ATP binding and hydrolysis are likely to induce conformational changes in the hairpin that are important for RNA unwinding or ribonucleoprotein remodelling. The structure of Prp43p provides the framework for functional and genetic analysis of all DEAH helicases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prp43p contains a processive helicase structural architecture with a specific regulatory domain.EMBO J. 2010 Jul 7;29(13):2194-204. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.102. Epub 2010 May 28. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20512115 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the DEAH/RHA ATPase Prp43p bound to RNA implicates a pair of hairpins and motif Va in translocation along RNA.RNA. 2017 Jul;23(7):1110-1124. doi: 10.1261/rna.060954.117. Epub 2017 Apr 17. RNA. 2017. PMID: 28416566 Free PMC article.
-
The crystal structure of human DEAH-box RNA helicase 15 reveals a domain organization of the mammalian DEAH/RHA family.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2017 Jun 1;73(Pt 6):347-355. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X17007336. Epub 2017 May 25. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2017. PMID: 28580923 Free PMC article.
-
Helicases involved in splicing from malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum.Parasitol Int. 2011 Dec;60(4):335-40. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2011.09.007. Epub 2011 Oct 1. Parasitol Int. 2011. PMID: 21996352 Review.
-
Studying structure and function of spliceosomal helicases.Methods. 2017 Aug 1;125:63-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2017.06.028. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Methods. 2017. PMID: 28668587 Review.
Cited by
-
DDX19A Promotes Metastasis of Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Inducing NOX1-Mediated ROS Production.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 22;11:629974. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.629974. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33968728 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of DEAH-box helicase 32 and its role in cancer.Oncol Lett. 2021 May;21(5):382. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12643. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33777205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fusarivirus accessory helicases present an evolutionary link for viruses infecting plants and fungi.Virol Sin. 2022 Jun;37(3):427-436. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2022.03.010. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Virol Sin. 2022. PMID: 35314402 Free PMC article.
-
RHAU helicase stabilizes G4 in its nucleotide-free state and destabilizes G4 upon ATP hydrolysis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jan 9;45(1):206-214. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw881. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28069994 Free PMC article.
-
SF1 and SF2 helicases: family matters.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2010 Jun;20(3):313-24. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2010.03.011. Epub 2010 Apr 22. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2010. PMID: 20456941 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams PD, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Hung LW, Ioerger TR, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Read RJ, Sacchettini JC, Sauter NK, Terwilliger TC (2002) PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 58: 1948–1954 - PubMed
-
- Alfano C, Sanfelice D, Babon J, Kelly G, Jacks A, Curry S, Conte MR (2004) Structural analysis of cooperative RNA binding by the La motif and central RRM domain of human La protein. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11: 323–329 - PubMed
-
- Andersen CBF, Ballut L, Johansen JS, Chamieh H, Nielsen KH, Oliveira C, Pedersen JS, Seraphin B, Le Hir H, Andersen GR (2006) Structure of the exon junction core complex with a trapped DEAD-Box ATPase bound to RNA. Science 313: 1968–1972 - PubMed
-
- Aravind L, Koonin EV (1999) G-patch: a new conserved domain in eukaryotic RNA-processing proteins and type D retroviral polyproteins. Trends Biochem Sci 24: 342–344 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

