Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors potentiate the rapid antidepressant-like effects of serotonin4 receptor agonists in the rat
- PMID: 20169084
- PMCID: PMC2821932
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009253
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors potentiate the rapid antidepressant-like effects of serotonin4 receptor agonists in the rat
Abstract
Background: We have recently reported that serotonin(4) (5-HT(4)) receptor agonists have a promising potential as fast-acting antidepressants. Here, we assess the extent to which this property may be optimized by the concomitant use of conventional antidepressants.
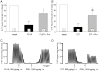
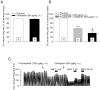
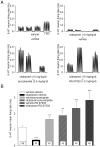
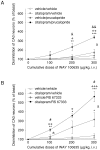
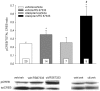
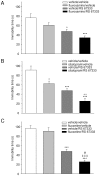
Methodology/principal findings: We found that, in acute conditions, the 5-HT(4) agonist prucalopride was able to counteract the inhibitory effect of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) fluvoxamine and citalopram on 5-HT neuron impulse flow, in Dorsal Raphé Nucleus (DRN) cells selected for their high (>1.8 Hz) basal discharge. The co-administration of both prucalopride and RS 67333 with citalopram for 3 days elicited an enhancement of DRN 5-HT neuron average firing rate, very similar to what was observed with either 5-HT(4) agonist alone. At the postsynaptic level, this translated into the manifestation of a tonus on hippocampal postsynaptic 5-HT(1A) receptors, that was two to three times stronger when the 5-HT(4) agonist was combined with citalopram. Similarly, co-administration of citalopram synergistically potentiated the enhancing effect of RS 67333 on CREB protein phosphorylation within the hippocampus. Finally, in the Forced Swimming Test, the combination of RS 67333 with various SSRIs (fluvoxamine, citalopram and fluoxetine) was more effective to reduce time of immobility than the separate administration of each compound.
Conclusions/significance: These findings strongly suggest that the adjunction of an SSRI to a 5-HT(4) agonist may help to optimize the fast-acting antidepressant efficacy of the latter.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serotonin(4) (5-HT(4)) receptor agonists are putative antidepressants with a rapid onset of action.Neuron. 2007 Sep 6;55(5):712-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.07.041. Neuron. 2007. PMID: 17785179
-
Assessment of the serotonin reuptake blocking property of YM992: electrophysiological studies in the rat hippocampus and dorsal raphe.Synapse. 1999 Dec 15;34(4):277-89. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(19991215)34:4<277::AID-SYN4>3.0.CO;2-W. Synapse. 1999. PMID: 10529722
-
Mechanism of action of the bimodal antidepressant vilazodone: evidence for serotonin1A-receptor-mediated auto-augmentation of extracellular serotonin output.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Jun;231(12):2547-58. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3428-7. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24419272
-
Comparison of the effects of antidepressants and their metabolites on reuptake of biogenic amines and on receptor binding.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1999 Aug;19(4):467-89. doi: 10.1023/a:1006986824213. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1999. PMID: 10379421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Escitalopram: a selective inhibitor and allosteric modulator of the serotonin transporter].Encephale. 2007 Dec;33(6):965-72. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2007.11.001. Epub 2007 Dec 11. Encephale. 2007. PMID: 18789789 Review. French.
Cited by
-
The role of 5-HT1A receptors in mediating acute negative effects of antidepressants: implications in pediatric depression.Transl Psychiatry. 2015 May 5;5(5):e563. doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.57. Transl Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25942044 Free PMC article.
-
The role of serotonin receptor subtypes in treating depression: a review of animal studies.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011 Feb;213(2-3):265-87. doi: 10.1007/s00213-010-2097-z. Epub 2010 Nov 24. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011. PMID: 21107537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rehabilitating a brain with Alzheimer's: a proposal.Clin Interv Aging. 2011;6:53-9. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S14008. Epub 2011 Feb 22. Clin Interv Aging. 2011. PMID: 21472092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural plasticity and proliferation in the generation of antidepressant effects: hippocampal implication.Neural Plast. 2013;2013:537265. doi: 10.1155/2013/537265. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Neural Plast. 2013. PMID: 23862076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of the Serotonergic Receptosome in the Treatment of Anxiety and Depression: A Narrative Review of the Experimental Evidence.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Feb 12;14(2):148. doi: 10.3390/ph14020148. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33673205 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kapur S, Remington G. Serotonin-dopamine interaction and its relevance to schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 1996;153:466–476. - PubMed
-
- Lengyel K, Pieschl R, Strong T, Molski T, Mattson G, et al. Ex vivo assessment of binding site occupancy of monoamine reuptake inhibitors: methodology and biological significance. Neuropharmacology. 2008;55:63–70. - PubMed
-
- Thase ME. What role do atypical antipsychotic drugs have in treatment-resistant depression? J Clin Psychiatry. 2002;63:95–103. - PubMed
-
- Shelton RC, Papakostas GI. Augmentation of antidepressants with atypical antipsychotics for treatment-resistant major depressive disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2008;117:253–259. - PubMed
-
- Trivedi MH. Treatment-resistant depression: new therapies on the horizon. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2003;15:59–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

