Telomeric heterochromatin in Plasmodium falciparum
- PMID: 20169127
- PMCID: PMC2821646
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/290501
Telomeric heterochromatin in Plasmodium falciparum
Abstract
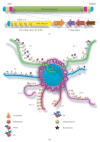
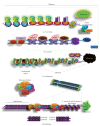
Until very recently, little was known about the chromatin structure of the telomeres and subtelomeric regions in Plasmodium falciparum. In yeast and Drosophila melanogaster, chromatin structure has long been known to be an important aspect in the regulation and functioning of these regions. Telomeres and subtelomeric regions are enriched in epigenetic marks that are specific to heterochromatin, such as methylation of lysine 9 of histone H3 and lysine 20 of histone H4. In P. falciparum, histone modifications and the presence of both the heterochromatin "writing" (PfSir2, PKMT) and "reading" (PfHP1) machinery at telomeric and subtelomeric regions indicate that these regions are likely to have heterochromatic structure that is epigenetically regulated. This structure may be important for telomere functions such as the silencing of the var gene family implicated in the cytoadherence and antigenic variation of these parasites.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

