Contributions of matrix metalloproteinases to neural plasticity, habituation, associative learning and drug addiction
- PMID: 20169175
- PMCID: PMC2821634
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/579382
Contributions of matrix metalloproteinases to neural plasticity, habituation, associative learning and drug addiction
Abstract
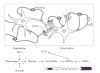
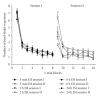
The premise of this paper is that increased expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) permits the reconfiguration of synaptic connections (i.e., neural plasticity) by degrading cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) designed to provide stability to those extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins that form scaffolding supporting neurons and glia. It is presumed that while these ECM proteins are weakened, and/or detached, synaptic connections can form resulting in new neural pathways. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) are designed to deactivate MMPs permitting the reestablishment of CAMs, thus returning the system to a reasonably fixed state. This review considers available findings concerning the roles of MMPs and TIMPs in reorganizing ECM proteins thus facilitating the neural plasticity underlying long-term potentiation (LTP), habituation, and associative learning. We conclude with a consideration of the influence of these phenomena on drug addiction, given that these same processes may be instrumental in the formation of addiction and subsequent relapse. However, our knowledge concerning the precise spatial and temporal relationships among the mechanisms of neural plasticity, habituation, associative learning, and memory consolidation is far from complete and the possibility that these phenomena mediate drug addiction is a new direction of research.
Figures
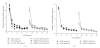
References
-
- Bliss TV, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361(6407):31–39. - PubMed
-
- Jorntell H, Hansel C. Synaptic memories upside down: bidirectional plasticity at cerebellar parallel fiber-purkinje cell synapses. Neuron. 2006;52(2):227–238. - PubMed
-
- Pastalkova E, Serrano P, Pinkhasova D, Wallace E, Fenton AA, Sacktor TC. Storage of spatial information by the maintenance mechanism of LTP. Science. 2006;313(5790):1141–1444. - PubMed
-
- Rioult-Pedotti M-S, Friedman D, Donoghue JP. Learning-induced LTP in neocortex. Science. 2000;290(5491):533–536. - PubMed
-
- Rogan MT, Staubli UV, LeDoux JE. Fear conditioning induces associative long-term potentiation in the amygdala. Nature. 1997;390(6660):604–607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

