The Syk kinase SmTK4 of Schistosoma mansoni is involved in the regulation of spermatogenesis and oogenesis
- PMID: 20169182
- PMCID: PMC2820527
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000769
The Syk kinase SmTK4 of Schistosoma mansoni is involved in the regulation of spermatogenesis and oogenesis
Abstract
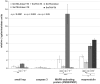
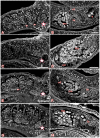
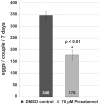
The signal transduction protein SmTK4 from Schistosoma mansoni belongs to the family of Syk kinases. In vertebrates, Syk kinases are known to play specialized roles in signaling pathways in cells of the hematopoietic system. Although Syk kinases were identified in some invertebrates, their role in this group of animals has not yet been elucidated. Since SmTK4 is the first Syk kinase from a parasitic helminth, shown to be predominantly expressed in the testes and ovary of adult worms, we investigated its function. To unravel signaling cascades in which SmTK4 is involved, yeast two-/three-hybrid library screenings were performed with either the tandem SH2-domain, or with the linker region including the tyrosine kinase domain of SmTK4. Besides the Src kinase SmTK3 we identified a new Src kinase (SmTK6) acting upstream of SmTK4 and a MAPK-activating protein, as well as mapmodulin acting downstream. Their identities and colocalization studies pointed to a role of SmTK4 in a signaling cascade regulating the proliferation and/or differentiation of cells in the gonads of schistosomes. To confirm this decisive role we performed biochemical and molecular approaches to knock down SmTK4 combined with a novel protocol for confocal laser scanning microscopy for morphological analyses. Using the Syk kinase-specific inhibitor Piceatannol or by RNAi treatment of adult schistosomes in vitro, corresponding phenotypes were detected in the testes and ovary. In the Xenopus oocyte system it was finally confirmed that Piceatannol suppressed the activity of the catalytic kinase domain of SmTK4. Our findings demonstrate a pivotal role of SmTK4 in gametogenesis, a new function for Syk kinases in eukaryotes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
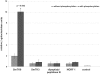
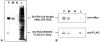
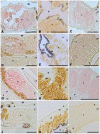
Similar articles
-
Characterization of the Src/Abl hybrid kinase SmTK6 of Schistosoma mansoni.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 9;286(49):42325-42336. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.210336. Epub 2011 Oct 19. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 22013071 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and first characterization of SmEps8, a potential interaction partner of SmTK3 and SER transcribed in the gonads of Schistosoma mansoni.Exp Parasitol. 2017 Sep;180:55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2016.12.002. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Exp Parasitol. 2017. PMID: 28017636
-
Discovery of platyhelminth-specific α/β-integrin families and evidence for their role in reproduction in Schistosoma mansoni.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52519. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052519. Epub 2012 Dec 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300694 Free PMC article.
-
Protein tyrosine kinase Syk in mast cell signaling.Mol Immunol. 2002 Sep;38(16-18):1229-33. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(02)00068-8. Mol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12217388 Review.
-
Structure and function of Syk protein-tyrosine kinase.J Biochem. 2001 Aug;130(2):177-86. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a002970. J Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11481033 Review.
Cited by
-
Transfection of Platyhelminthes.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:206161. doi: 10.1155/2015/206161. Epub 2015 May 18. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26090388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of signal peptidase complex expression affects the development and survival of Schistosoma japonicum.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Mar 3;13:1136056. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1136056. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36936776 Free PMC article.
-
Sensory Protein Kinase Signaling in Schistosoma mansoni Cercariae: Host Location and Invasion.J Infect Dis. 2015 Dec 1;212(11):1787-97. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv464. Epub 2015 Sep 23. J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26401028 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of fs800 on female egg production in Schistosoma mansoni.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2021 Sep;245:111412. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2021.111412. Epub 2021 Sep 4. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2021. PMID: 34492240 Free PMC article.
-
Dual targeting of insulin and venus kinase Receptors of Schistosoma mansoni for novel anti-schistosome therapy.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013 May 16;7(5):e2226. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002226. Print 2013. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013. PMID: 23696913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chitsulo L, LoVerde PT, Engels D. Schistosomiasis. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2:12–13. - PubMed
-
- Quack T, Beckmann S, Grevelding CG. Schistosomiasis and the molecular biology of the male-female interaction of S. mansoni. BMTW. 2006;119:365–372. - PubMed
-
- Ross AG, Bartley PB, Sleigh AC, Olds GR, Li Y, et al. Schistosomiasis. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1212–1220. - PubMed
-
- Fenwick A, Webster JP. Schistosomiasis: challenges for control, treatment and drug resistance. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2006;19:577–582. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

