Raptor is phosphorylated by cdc2 during mitosis
- PMID: 20169205
- PMCID: PMC2820552
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009197
Raptor is phosphorylated by cdc2 during mitosis
Abstract
Background: The appropriate control of mitotic entry and exit is reliant on a series of interlocking signaling events that coordinately drive the biological processes required for accurate cell division. Overlaid onto these signals that promote orchestrated cell division are checkpoints that ensure appropriate mitotic spindle formation, a lack of DNA damage, kinetochore attachment, and that each daughter cell has the appropriate complement of DNA. We recently discovered that AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) modulates the G2/M phase of cell cycle progression in part through its suppression of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling. AMPK directly phosphorylates the critical mTOR binding partner raptor inhibiting mTORC1 (mTOR-raptor rapamycin sensitive mTOR kinase complex 1). As mTOR has been previously tied to mitotic control, we examined further how raptor may contribute to this process.
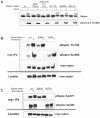
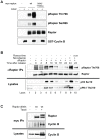
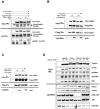
Methodology/principal findings: We have discovered that raptor becomes highly phosphorylated in cells in mitosis. Utilizing tandem mass spectrometry, we identified a number of novel phosphorylation sites in raptor, and using phospho-specific antibodies demonstrated that raptor becomes phosphorylated on phospho-serine/threonine-proline sites in mitosis. A combination of site-directed mutagenesis in a tagged raptor cDNA and analysis with a series of new phospho-specific antibodies generated against different sites in raptor revealed that Serine 696 and Threonine 706 represent two key sites in raptor phosphorylated in mitosis. We demonstrate that the mitotic cyclin-dependent kinase cdc2/CDK1 is the kinase responsible for phosphorylating these sites, and its mitotic partner Cyclin B efficiently coimmunoprecipitates with raptor in mitotic cells.
Conclusions/significance: This study demonstrates that the key mTOR binding partner raptor is directly phosphorylated during mitosis by cdc2. This reinforces previous studies suggesting that mTOR activity is highly regulated and important for mitotic progression, and points to a direct modulation of the mTORC1 complex during mitosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mitotic raptor promotes mTORC1 activity, G(2)/M cell cycle progression, and internal ribosome entry site-mediated mRNA translation.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Jul;30(13):3151-64. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00322-09. Epub 2010 May 3. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20439490 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal cell kinase (ICK) promotes activation of mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) through phosphorylation of Raptor Thr-908.J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 6;287(15):12510-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.302117. Epub 2012 Feb 22. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22356909 Free PMC article.
-
Raptor, a positive regulatory subunit of mTOR complex 1, is a novel phosphoprotein of the rDNA transcription machinery in nucleoli and chromosomal nucleolus organizer regions (NORs).Cell Cycle. 2011 Sep 15;10(18):3140-52. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.18.17376. Epub 2011 Sep 15. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 21900751
-
The overlooked greatwall: a new perspective on mitotic control.Open Biol. 2012 Mar;2(3):120023. doi: 10.1098/rsob.120023. Open Biol. 2012. PMID: 22754657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The decision to enter mitosis: feedback and redundancy in the mitotic entry network.J Cell Biol. 2009 Apr 20;185(2):193-202. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200812045. Epub 2009 Apr 13. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19364923 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of mTORC1 by Upstream Stimuli.Genes (Basel). 2020 Aug 25;11(9):989. doi: 10.3390/genes11090989. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32854217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Roles of Post-Translational Modifications on mTOR Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 11;22(4):1784. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041784. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33670113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ser2481-autophosphorylated mTOR colocalizes with chromosomal passenger proteins during mammalian cell cytokinesis.Cell Cycle. 2012 Nov 15;11(22):4211-21. doi: 10.4161/cc.22551. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 23095638 Free PMC article.
-
Mitotic CDK1 and 4E-BP1 II: A single phosphomimetic mutation in 4E-BP1 induces glucose intolerance in mice.PLoS One. 2023 Mar 10;18(3):e0282914. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282914. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36897840 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of insulin-stimulated 4E-BP protein binding to mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) complex 1 and its contribution to mTOR complex 1 signaling.J Biol Chem. 2011 Nov 4;286(44):38043-38053. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.245449. Epub 2011 Sep 13. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21914810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wullschleger S, Loewith R, Hall MN. TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell. 2006;124:471–484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

