Inv acts as a molecular anchor for Nphp3 and Nek8 in the proximal segment of primary cilia
- PMID: 20169535
- PMCID: PMC9134828
- DOI: 10.1002/cm.20428
Inv acts as a molecular anchor for Nphp3 and Nek8 in the proximal segment of primary cilia
Abstract
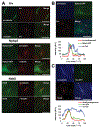
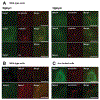
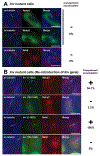
A primary cilium is an antenna-like structure extending from the surface of most vertebrate cells. It is structurally divided along its vertical axis into sub-compartments that include the ciliary tip, the shaft, the ciliary necklace segment, the transitional zone and the basal body. We recently discovered that the shaft of the primary cilia has a distinct molecular compartment, termed the "Inv compartment", which is characterized by the accumulation of Inv at the base of primary cilia. Inv was discovered as a causative gene in inv mutant mice. It was later found to be responsible for the infantile type of nephronophthisis (NPHP2). Nephronophthisis (NPHP) is an autosomal recessive kidney disease. Nine causative genes have been identified, with all examined products thought to function in cilia, basal body and/or centrioles. However, their exact intra-ciliary localization and relationship have not been clear. Here, we report that products of Nphp3 and Nek8 (the mouse orthologs of the causative genes for NPHP3 and NPHP9, respectively) localize to the Inv compartment. We also show that Inv is essential for the compartmental localization of Nphp3 and Nek8, whereas localization of Inv does not require Nphp3 or Nek8. Nphp1 and Nphp4 also localize at the proximal region of the cilium, but not in Inv compartment. Our results indicate that Inv acts as an anchor for Nphp3 and Nek8 in the Inv compartment, and suggest that Inv compartment is a candidate site for intra-ciliary interaction of Inv, Nphp3 and Nek8.
2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Arts HH, Doherty D, van Beersum SE, Parisi MA, Letteboer SJ, Gorden NT, Peters TA, Marker T, Voesenek K, Kartono A, Ozyurek H, Farin FM, Kroes HY, Wolfrum U, Brunner HG, Cremers FP, Glass IA, Knoers NV, Roepman R. 2007. Mutations in the gene encoding the basal body protein RPGRIP1L, a nephrocystin-4 interactor, cause Joubert syndrome. Nat Genet 39(7):882–888. - PubMed
-
- Attanasio M, Uhlenhaut NH, Sousa VH, O’Toole JF, Otto E, Anlag K, Klugmann C, Treier AC, Helou J, Sayer JA, Seelow D, Nurnberg G, Becker C, Chudley AE, Nurnberg P, Hildebrandt F, Treier M. 2007. Loss of GLIS2 causes nephronophthisis in humans and mice by increased apoptosis and fibrosis. Nat Genet 39(8):1018–1024. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann C, Fliegauf M, Bruchle NO, Frank V, Olbrich H, Kirschner J, Schermer B, Schmedding I, Kispert A, Kranzlin B, Nurnberg G, Becker C, Grimm T, Girschick G, Lynch SA, Kelehan P, Senderek J, Neuhaus TJ, Stallmach T, Zentgraf H, Nurnberg P, Gretz N, Lo C, Lienkamp S, Schafer T, Walz G, Benzing T, Zerres K, Omran H. 2008. Loss of nephrocystin-3 function can cause embryonic lethality, Meckel-Gruber-like syndrome, situs inversus, and renal-hepatic-pancreatic dysplasia. Am J Hum Genet 82(4): 959–970. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bowers AJ, Boylan JF. 2004. Nek8, a NIMA family kinase member, is over-expressed in primary human breast tumors. Gene 328:135–142. - PubMed
-
- Deane JA, Cole DG, Seeley ES, Diener DR, Rosenbaum JL. 2001. Localization of intraflagellar transport protein IFT52 identifies basal body transitional fibers as the docking site for IFT particles. Curr Biol 11(20): 1586–1590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

