Chrysophanol induces necrosis through the production of ROS and alteration of ATP levels in J5 human liver cancer cells
- PMID: 20169580
- PMCID: PMC3031088
- DOI: 10.1002/mnfr.200900265
Chrysophanol induces necrosis through the production of ROS and alteration of ATP levels in J5 human liver cancer cells
Abstract
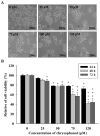
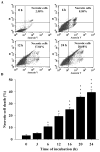
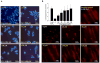
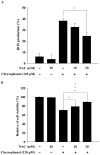
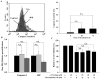
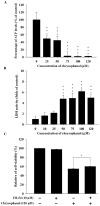
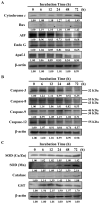
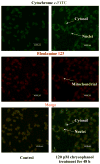
Anthraquinone compounds have been shown to induce apoptosis in different cancer cell types. Effects of chrysophanol, an anthraquinone compound, on cancer cell death have not been well studied. The goal of this study was to examine if chrysophanol had cytotoxic effects and if such effects involved apoptosis or necrosis in J5 human liver cancer cells. Chrysophanol induced necrosis in J5 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Non-apoptotic cell death was induced by chrysophanol in J5 cells and was characterized by caspase independence, delayed externalization of phosphatidylserine and plasma membrane disruption. Blockage of apoptotic induction by a general caspase inhibitor (z-VAD-fmk) failed to protect cells against chrysophanol-induced cell death. The levels of reactive oxygen species production and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (DeltaPsi(m)) were also determined to assess the effects of chrysophanol. However, reductions in adenosine triphosphate levels and increases in lactate dehydrogenase activity indicated that chrysophanol stimulated necrotic cell death. In summary, human liver cancer cells treated with chrysophanol exhibited a cellular pattern associated with necrosis and not apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
A note on the relevance of chrysophanol to food and anticancer research.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2012 Jun;56(6):843. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201270044. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2012. PMID: 22707259 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Chrysophanol-induced cell death (necrosis) in human lung cancer A549 cells is mediated through increasing reactive oxygen species and decreasing the level of mitochondrial membrane potential.Environ Toxicol. 2014 May;29(7):740-9. doi: 10.1002/tox.21801. Epub 2012 Jul 30. Environ Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 22848001
-
Mitochondrial-dependent caspase activation pathway is involved in baicalein-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma J5 cells.Int J Oncol. 2009 Oct;35(4):717-24. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000384. Int J Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19724907
-
Chrysophanol-induced necrotic-like cell death through an impaired mitochondrial ATP synthesis in Hep3B human liver cancer cells.Arch Pharm Res. 2012 May;35(5):887-95. doi: 10.1007/s12272-012-0514-z. Epub 2012 May 29. Arch Pharm Res. 2012. PMID: 22644856
-
Reactive oxygen species accumulation contributes to gambogic acid-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma SMMC-7721 cells.Toxicology. 2009 Jun 16;260(1-3):60-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2009.03.010. Epub 2009 Mar 24. Toxicology. 2009. PMID: 19464570
-
Inhibition of apoptosis facilitates necrosis induced by cisplatin in gastric cancer cells.Anticancer Drugs. 2008 Feb;19(2):159-66. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e3282f30d05. Anticancer Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18176112
Cited by
-
Comparison of the Phytochemical Properties, Antioxidant Activity and Cytotoxic Effect on HepG2 Cells in Mongolian and Taiwanese Rhubarb Species.Molecules. 2021 Feb 25;26(5):1217. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051217. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33668690 Free PMC article.
-
Phenethyl Isothiocyanate (PEITC) Inhibits the Growth of Human Oral Squamous Carcinoma HSC-3 Cells through G(0)/G(1) Phase Arrest and Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptotic Cell Death.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:718320. doi: 10.1155/2012/718320. Epub 2012 Jul 10. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012. PMID: 22919418 Free PMC article.
-
Evening Primrose Oil Improves Chemotherapeutic Effects in Human Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines-A Preclinical Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Apr 12;15(4):466. doi: 10.3390/ph15040466. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455464 Free PMC article.
-
Chrysophanol alleviates myocardial injury in diabetic db/db mice by regulating the SIRT1/HMGB1/NF-κB signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Dec;18(6):4406-4412. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8083. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31772635 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Role of Dahuang in Hepatoma Treatment Using Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Survival Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 15;2022:5975223. doi: 10.1155/2022/5975223. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35872841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A, Kroemer G. Self-eating and self-killing: crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:741–752. - PubMed
-
- Arends MJ, Wyllie AH. Apoptosis: mechanisms and roles in pathology. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1991;32:223–254. - PubMed
-
- Okada H, Mak TW. Pathways of apoptotic and non-apoptotic death in tumour cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:592–603. - PubMed
-
- Wada A, Fukui K, Sawai Y, Imanaka K, et al. Pamidronate induced anti-proliferative, apoptotic, and anti-migratory effects in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2006;44:142–150. - PubMed
-
- Rougier P, Mitry E, Barbare JC, Taieb J. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): an update. Semin Oncol. 2007;34:S12–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

