Development of novel adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activators
- PMID: 20170185
- PMCID: PMC2841718
- DOI: 10.1021/jm901773d
Development of novel adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activators
Retraction in
-
Retraction of "Development of Novel Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Activators".J Med Chem. 2018 Jun 14;61(11):5055. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00707. Epub 2018 May 18. J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29772897 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
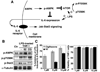
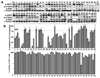
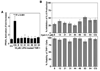
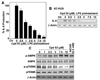
In light of the unique ability of thiazolidinediones to mediate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)gamma-independent activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and suppression of interleukin (IL)-6 production, we conducted a screening of an in-house, thiazolidinedione-based focused compound library to identify novel agents with these dual pharmacological activities. Cell-based assays pertinent to the activation status of AMPK and mammalian homologue of target of rapamycin (i.e., phosphorylation of AMPK and p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase, respectively) and IL-6/IL-6 receptor signaling (i.e., IL-6 production and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 phosphorylation, respectively) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated THP-1 human macrophages were used to screen this compound library, which led to the identification of compound 53 (N-{4-[3-(1-methyl-cyclohexylmethyl)-2,4-dioxo-thiazolidin-5-ylidene-methyl]-phenyl}-4-nitro-3-trifluoro-methyl-benzenesulfonamide) as the lead agent. Evidence indicates that this drug-induced suppression of LPS-stimulated IL-6 production was attributable to AMPK activation. Furthermore, compound 53-mediated AMPK activation was demonstrated in C-26 colon adenocarcinoma cells, indicating that it is not a cell line-specific event.
Figures


References
-
- Kahn BB, Alquier T, Carling D, Hardie DG. AMP-activated protein kinase: ancient energy gauge provides clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab. 2005;1:15–25. - PubMed
-
- Hardie DG, Sakamoto K. AMPK: a key sensor of fuel and energy status in skeletal muscle. Physiology (Bethesda) 2006;21:48–60. - PubMed
-
- Hardie DG. AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:774–785. - PubMed
-
- Inoki K, Zhu T, Guan KL. TSC2 mediates cellular energy response to control cell growth and survival. Cell. 2003;115:577–590. - PubMed
-
- Lihn AS, Pedersen SB, Lund S, Richelsen B. The anti-diabetic AMPK activator AICAR reduces IL-6 and IL-8 in human adipose tissue and skeletal muscle cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008;292:36–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

