Novel induced mlo mutant alleles in combination with site-directed mutagenesis reveal functionally important domains in the heptahelical barley Mlo protein
- PMID: 20170486
- PMCID: PMC2844067
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-31
Novel induced mlo mutant alleles in combination with site-directed mutagenesis reveal functionally important domains in the heptahelical barley Mlo protein
Abstract
Background: Recessively inherited natural and induced mutations in the barley Mlo gene confer durable broad-spectrum resistance against the powdery mildew pathogen, Blumeria graminis f.sp. hordei. Mlo codes for a member of a plant-specific family of polytopic integral membrane proteins with unknown biochemical activity. Resistant barley mlo mutant alleles identify amino acid residues that are critical for Mlo function in the context of powdery mildew susceptibility.
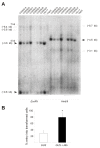
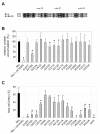
Results: We molecularly analyzed a novel set of induced barley mlo mutants and used site-directed mutagenesis in combination with transient gene expression to unravel novel amino acid residues of functional significance. We integrate these results with previous findings to map functionally important regions of the heptahelical Mlo protein. Our data reveal the second and third cytoplasmic loop as being particularly sensitive to functional impediment by mutational perturbation, suggesting that these regions are critical for the susceptibility-conferring activity of the Mlo protein. In contrast, only mutations in the second but not the third cytoplasmic loop appear to trigger the Endoplasmic Reticulum-localized quality control machinery that ensures the biogenesis of properly folded membrane proteins.
Conclusion: Our findings identify functionally important regions of the polytopic barley Mlo protein and reveal the differential sensitivity of individual protein domains to cellular quality control.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Magical mystery tour: MLO proteins in plant immunity and beyond.New Phytol. 2014 Oct;204(2):273-81. doi: 10.1111/nph.12889. New Phytol. 2014. PMID: 25453131 Review.
-
Barley Ror1 encodes a class XI myosin required for mlo-based broad-spectrum resistance to the fungal powdery mildew pathogen.Plant J. 2022 Oct;112(1):84-103. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15930. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Plant J. 2022. PMID: 35916711
-
Physiological Changes in Barley mlo-11 Powdery Mildew Resistance Conditioned by Tandem Repeat Copy Number.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 20;21(22):8769. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228769. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33233522 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Gun-Mediated Transient Gene Expression for Functional Studies in Plant Immunity.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2523:63-77. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2449-4_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35759191
-
Serpentine plant MLO proteins as entry portals for powdery mildew fungi.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Apr;33(Pt 2):389-92. doi: 10.1042/BST0330389. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 15787613 Review.
Cited by
-
CmMLO17 and its partner CmKIC potentially support Alternaria alternata growth in Chrysanthemum morifolium.Hortic Res. 2021 May 1;8(1):101. doi: 10.1038/s41438-021-00534-x. Hortic Res. 2021. PMID: 33931614 Free PMC article.
-
A trade off between mlo resistance to powdery mildew and increased susceptibility of barley to a newly important disease, Ramularia leaf spot.J Exp Bot. 2014 Mar;65(4):1025-37. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert452. Epub 2014 Jan 7. J Exp Bot. 2014. PMID: 24399175 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative phylogenetic analysis of genome-wide Mlo gene family members from Glycine max and Arabidopsis thaliana.Mol Genet Genomics. 2014 Jun;289(3):345-59. doi: 10.1007/s00438-014-0811-y. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Mol Genet Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24469270
-
mlo-based powdery mildew resistance in hexaploid bread wheat generated by a non-transgenic TILLING approach.Plant Biotechnol J. 2017 Mar;15(3):367-378. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12631. Epub 2016 Sep 25. Plant Biotechnol J. 2017. PMID: 27565953 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and Characterization of a Novel Tomato mlo Mutant from an EMS Mutagenized Micro-Tom Population.Genes (Basel). 2021 May 11;12(5):719. doi: 10.3390/genes12050719. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34064921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jørgensen JH. Genetics of powdery mildew resistance in barley. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 1994;13:97–119. doi: 10.1080/713608055. - DOI
-
- Jørgensen JH. Discovery, characterization and exploitation of Mlo powdery mildew resistance in barley. Euphytica. 1992;63:141–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00023919. - DOI
-
- Lyngkjaer MF, Newton AC, Atzema JL, Baker SJ. The barley mlo-gene: an important powdery mildew resistance source. Agronomie. 2000;20:745–756. doi: 10.1051/agro:2000173. - DOI
-
- Freisleben R, Lein A. Über die Auffindung einer mehltauresistenten Mutante nach Röntgenbestrahlung einer anfälligen reinen Linie von Sommergerste. Naturwissenschaften. 1942;30:608. doi: 10.1007/BF01488231. - DOI
-
- Hänsel H, Zakovsky J. Röntgeninduzierte Mutanten der Vollkorngerste. Bodenkultur. 1957;9:50–64.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

