Upstream molecular signaling pathways of p27(Kip1) expression: effects of 4-hydroxytamoxifen, dexamethasone, and retinoic acids
- PMID: 20170512
- PMCID: PMC2841156
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2867-10-3
Upstream molecular signaling pathways of p27(Kip1) expression: effects of 4-hydroxytamoxifen, dexamethasone, and retinoic acids
Abstract
Background: p27(Kip1) is a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor that inhibits G1-to-S phase transition of the cell cycle. It is known that a relatively large number of nutritional and chemopreventive anti-cancer agents specifically up-regulate expression of p27 without directly affecting the expression of other G1-to-S phase cell cycle regulatory proteins including p21(Cip1Waf1). However, the upstream molecular signaling pathways of how these agents up-regulate the expression of p27 have not been well characterized. The objective of this study was to identify such pathways in human breast cancer cells in vitro using 4-hydroxytamoxifen, dexamethasone, and various retinoic acids as examples of such anti-cancer agents.
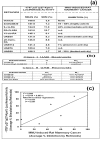
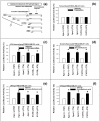
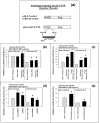
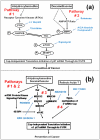
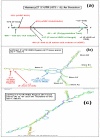
Results: Experimental evidence presented in the first half of this report was obtained by transfecting human breast cancer cells in vitro with proximal upstream region of p27 gene-luciferase reporter plasmids. 1) The evidence indicated that 4-hydroxytamoxifen, dexamethasone, and various retinoic acids up-regulated expression of p27 in both estrogen receptor-positive and negative human breast cancer cells in vitro. 2) The degree of up-regulation of p27 expression by these anti-cancer agents in human breast cancer cells in vitro linearly correlated with the degree of inhibition of methylnitrosourea (MNU)-induced rat mammary adenocarcinoma in vivo. 3) Lastly, up-regulation of the expression of p27 was likely due to the activation of translation initiation rather than transcription of p27 gene. The experimental evidence presented in the second half of this report was obtained by a combination of Western immunoblot analysis and transfection analysis. It indicated that 4-hydroxytamoxifen and dexamethasone up-regulated expression of p27 by down-regulating phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E)-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1) at Ser65 and this phosphorylation was likely to be mediated by upstream receptor tyrosine kinases/phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Akt/5'-AMP-activated protein kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin (RTKs/PI3K/Akt/AMPK/mTOR) protein kinase signaling pathways. Retinoic acids up-regulated expression of p27 without using either 4E-BP1 or RTKs/PI3K/Akt/AMPK/mTOR protein kinase signaling pathways.
Conclusions: 4-Hydroxytamoxifen and dexamethasone up-regulated translation initiation of p27 by down-regulating 4E-BP1 phosphorylated at Ser65 and this down-regulation seemed to be mediated by upstream RTKs/PI3K/Akt/AMPK/mTOR protein kinase signaling pathways. Retinoic acids also up-regulated translation initiation of p27, but without using any of these pathways.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Upstream molecular signaling pathways of p27(Kip1) expression in human breast cancer cells in vitro: differential effects of 4-hydroxytamoxifen and deficiency of either D-(+)-glucose or L-leucine.Cancer Cell Int. 2011 Sep 9;11:31. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-11-31. Cancer Cell Int. 2011. PMID: 21906315 Free PMC article.
-
"Nutritional and chemopreventive anti-cancer agents up-regulate expression of p27Kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, in mouse JB6 epidermal and human MCF7, MDA-MB-321 and AU565 breast cancer cells".Cancer Cell Int. 2006 Aug 9;6:20. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-6-20. Cancer Cell Int. 2006. PMID: 16899133 Free PMC article.
-
BCR/ABL regulates expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 through the phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/AKT pathway.J Biol Chem. 2000 Dec 15;275(50):39223-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M007291200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 11010972
-
4E-BP1, a multifactor regulated multifunctional protein.Cell Cycle. 2016;15(6):781-6. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1151581. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 26901143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights into Notch1 regulation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR1 signaling axis: targeted therapy of γ-secretase inhibitor resistant T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Cell Signal. 2014 Jan;26(1):149-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.09.021. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24140475 Review.
Cited by
-
Upstream molecular signaling pathways of p27(Kip1) expression in human breast cancer cells in vitro: differential effects of 4-hydroxytamoxifen and deficiency of either D-(+)-glucose or L-leucine.Cancer Cell Int. 2011 Sep 9;11:31. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-11-31. Cancer Cell Int. 2011. PMID: 21906315 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of p27Kip1, a cell cycle repressor protein, is inversely associated with potential carcinogenic risk in the genetic rodent models of obesity and long-lived Ames dwarf mice.Metabolism. 2013 Jun;62(6):873-87. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.01.001. Epub 2013 Jan 26. Metabolism. 2013. PMID: 23357529 Free PMC article.
-
Sirt7-p21 Signaling Pathway Mediates Glucocorticoid-Induced Inhibition of Mouse Neural Stem Cell Proliferation.Neurotox Res. 2021 Apr;39(2):444-455. doi: 10.1007/s12640-020-00294-x. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Neurotox Res. 2021. PMID: 33025360
-
Potential Therapeutic Roles for Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway in the Pathophysiology of Diabetic Retinopathy.J Ophthalmol. 2011;2011:589813. doi: 10.1155/2011/589813. Epub 2011 Oct 30. J Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 22132311 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting gender-based biomarkers and drug targets: advancing personalized therapeutic strategies in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 20;15:1433540. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1433540. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38966543 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

