Analysis of the DNA translocation and unwinding activities of T4 phage helicases
- PMID: 20170733
- PMCID: PMC2919206
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2010.02.011
Analysis of the DNA translocation and unwinding activities of T4 phage helicases
Abstract
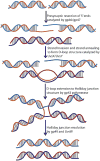
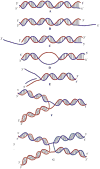
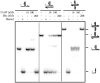
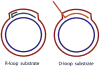
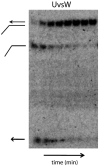
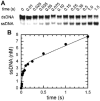
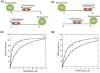
Helicases are an important class of enzymes involved in DNA and RNA metabolism that couple the energy of ATP hydrolysis to unwind duplex DNA and RNA structures. Understanding the mechanism of helicase action is vital due to their involvement in various biological processes such as DNA replication, repair and recombination. Furthermore, the duplex DNA unwinding property of this class of enzymes is closely related to their single-stranded DNA translocation. Hence the study of its translocation properties is essential to understanding helicase activity. Here we review the methods that are employed to analyze the DNA translocation and unwinding activities of the bacteriophage T4 UvsW and Dda helicases. These methods have been successfully employed to study the functions of helicases from large superfamilies.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
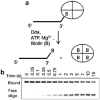

References
-
- Singleton MR, Dillingham MS, Wigley DB. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:23–50. - PubMed
-
- Ellis NA. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1997;7:354–363. - PubMed
-
- Nelson SW, Zhuang Z, Spiering MM, Benkovic SJ. T4 Phage Replisome. In: Cameron C, editor. Viral Genome Replication. Springer; New Jersey: 2009. pp. 349–376.
-
- Liu CC, Alberts BM. J Biol Chem. 1981;256:2813–2820. - PubMed
-
- Young MC, Schultz DE, Ring D, von Hippel PH. J Mol Biol. 1994;235:1447–1458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

