Angiotensin-converting enzymes and drug discovery in cardiovascular diseases
- PMID: 20170743
- PMCID: PMC3005694
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2010.02.003
Angiotensin-converting enzymes and drug discovery in cardiovascular diseases
Abstract
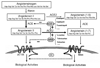
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) is a major target in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). In addition to ACE, ACE2 - which is a homolog of ACE and promotes the degradation of angiotensin II (Ang II) to Ang (1-7) - has been recognized recently as a potential therapeutic target in the management of CVDs. This article reviews different metabolic pathways of ACE and ACE2 (Ang I-Ang II-AT1 receptors and Ang I-Ang (1-7)-Mas receptors) in the regulation of cardiovascular function and their potential in new drug development in the therapy of CVDs. In addition, recent progress in the study of angiotensin and ACE in fetal origins of CVD, which might present an interesting field in perinatal medicine and preventive medicine, is briefly summarized.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Paul M, et al. Physiology of local renin-angiotensin systems. Physiol. Rev. 2006;86:747–803. - PubMed
-
- Brede M, Hein L. Transgenic mouse models of angiotensin receptor subtype function in the cardiovascular system. Regul. Pept. 2001;96:125–132. - PubMed
-
- Levy BI. Can angiotensin II type 2 receptors have deleterious effects in cardiovascular disease? Implications for therapeutic blockade of the renin-angiotensin system. Circulation. 2004;109:8–13. - PubMed
-
- Steckelings UM, et al. The AT2 receptor: a matter of love and hate. Peptides. 2005;26:1401–1409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

