Arabidopsis dynamin-related protein 1A polymers bind, but do not tubulate, liposomes
- PMID: 20171176
- PMCID: PMC2874938
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.02.070
Arabidopsis dynamin-related protein 1A polymers bind, but do not tubulate, liposomes
Abstract
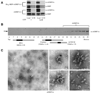
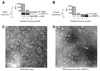
The Arabidopsis dynamin-related protein 1A (AtDRP1A) is involved in endocytosis and cell plate maturation in Arabidopsis. Unlike dynamin, AtDRP1A does not have any recognized membrane binding or protein-protein interaction domains. We report that GTPase active AtDRP1A purified from Escherichia coli as a fusion to maltose binding protein forms homopolymers visible by negative staining electron microscopy. These polymers interact with protein-free liposomes whose lipid composition mimics that of the inner leaflet of the Arabidopsis plasma membrane, suggesting that lipid-binding may play a role in AtDRP1A function. However, AtDRP1A polymers do not appear to assemble and disassemble in a dynamic fashion and do not have the ability to tubulate liposomes in vitro, suggesting that additional factors or modifications are necessary for AtDRP1A's in vivo function.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Collings DA, Gebbie LK, Howles PA, Hurley UA, Birch RJ, Cork AH, Hocart CH, Arioli T, Williamson RE. Arabidopsis dynamin-like protein DRP1A: a null mutant with widespread defects in endocytosis, cellulose synthesis, cytokinesis, and cell expansion. J. Exp. Bot. 2008;59:361–376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

