Radiation dose-volume effects in the brain
- PMID: 20171513
- PMCID: PMC3554255
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.02.091
Radiation dose-volume effects in the brain
Abstract
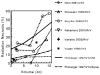
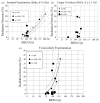
We have reviewed the published data regarding radiotherapy (RT)-induced brain injury. Radiation necrosis appears a median of 1-2 years after RT; however, cognitive decline develops over many years. The incidence and severity is dose and volume dependent and can also be increased by chemotherapy, age, diabetes, and spatial factors. For fractionated RT with a fraction size of <2.5 Gy, an incidence of radiation necrosis of 5% and 10% is predicted to occur at a biologically effective dose of 120 Gy (range, 100-140) and 150 Gy (range, 140-170), respectively. For twice-daily fractionation, a steep increase in toxicity appears to occur when the biologically effective dose is >80 Gy. For large fraction sizes (>or=2.5 Gy), the incidence and severity of toxicity is unpredictable. For single fraction radiosurgery, a clear correlation has been demonstrated between the target size and the risk of adverse events. Substantial variation among different centers' reported outcomes have prevented us from making toxicity-risk predictions. Cognitive dysfunction in children is largely seen for whole brain doses of >or=18 Gy. No substantial evidence has shown that RT induces irreversible cognitive decline in adults within 4 years of RT.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: none.
Figures
References
-
- Lax I, Karlsson B. Prediction of complications in gamma knife radiosurgery of arteriovenous malformation. Acta Oncol. 1996;35:49–55. - PubMed
-
- Voges J, Treuer H, Sturm V, et al. Risk analysis of linear accelerator radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996;36:1055–1063. - PubMed
-
- Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Pollock BE, et al. Complications from arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery: Multivariate analysis and risk modeling. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997;38:485–490. - PubMed
-
- Miyawaki L, Dowd C, Wara W, et al. Five year results of LINAC radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations: Outcome for large AVMS. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999;44:1089–1106. - PubMed
-
- Chin LS, Ma L, DiBiase S. Radiation necrosis following gamma knife surgery: A case-controlled comparison of treatment parameters and long-term clinical follow up. J Neurosurg. 2001;94:899–904. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

