Radiation-associated liver injury
- PMID: 20171524
- PMCID: PMC4388033
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.06.092
Radiation-associated liver injury
Abstract
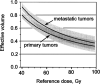
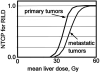
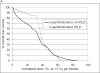
The liver is a critically important organ that has numerous functions including the production of bile, metabolism of ingested nutrients, elimination of many waste products, glycogen storage, and plasma protein synthesis. The liver is often incidentally irradiated during radiation therapy (RT) for tumors in the upper- abdomen, right lower lung, distal esophagus, or during whole abdomen or whole body RT. This article describes the endpoints, time-course, and dose-volume effect of radiation on the liver.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Yamasaki SA, Marn CS, Francis IR, et al. High-dose localized radiation therapy for treatment of hepatic malignant tumors: CT findings and their relation to radiation hepatitis. AJR American Journal of Roentgenology. 1995;165:79–84. - PubMed
-
- Lawrence TS, Robertson JM, Anscher MS, et al. Hepatic toxicity resulting from cancer treatment. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics. 1995;31:1237–1248. - PubMed
-
- Xu Z-Y, Liang S-X, Zhu J, et al. Prediction of radiation-induced liver disease by Lyman normal-tissue complication probability model in three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy for primary liver carcinoma. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics. 2006;65:189–195. - PubMed
-
- Kim TH, Kim DY, Park J-W, et al. Dose-volumetric parameters predicting radiation-induced hepatic toxicity in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics. 2007;67:225–231. - PubMed
-
- Cheng JC-H, Wu J-K, Huang C-M, et al. Radiation-induced liver disease after three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: dosimetric analysis and implication. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics. 2002;54:156–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

