Bladder afferent signaling: recent findings
- PMID: 20171668
- PMCID: PMC3686308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.12.060
Bladder afferent signaling: recent findings
Abstract
Purpose: Much current research on lower urinary tract physiology focuses on afferent mechanisms. The main goals are to define and control the signaling pathways by which afferent information is generated and conveyed to the central nervous system. We summarize recent research on bladder afferent mechanisms.
Materials and methods: We systematically reviewed the literature by searching PubMed up to June 2009 with focus on the last 5 years.
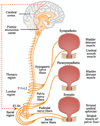
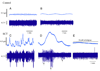
Results: At least 2 signaling pathways can be identified, including the urothelial and the myogenic pathway. The urothelial pathway is a functional unit consisting of the urothelium, interstitial cells and afferent nerves in the lamina propria. Signaling occurs via muscle-mucosal mechanoreceptors, mucosal mechanoreceptors and chemoreceptors. The myogenic pathway is activated via in-series mechanoreceptors responding to distention and via spontaneous contractile activity in units of myocytes generating afferent noise.
Conclusions: To control dysfunctional micturition we must know more about all components involved in normal micturition control, including how afferent information is handled by the central nervous system.
Copyright (c) 2010 American Urological Association Education and Research, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

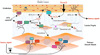
References
-
- Andersson KE, Arner A. Urinary bladder contraction and relaxation: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:935. - PubMed
-
- Drake MJ, Mills IW, Gillespie JI. Model of peripheral autonomous modules and a myovesical plexus in normal and overactive bladder function. Lancet. 2001;358:401. - PubMed
-
- Yoshimura N, Kaiho Y, Miyazato M, et al. Therapeutic receptor targets for lower urinary tract dysfunction. Naunyn Schmied Arch Pharmacol. 2008;377:437. - PubMed
-
- Wakabayashi Y, Tomoyoshi T, Fujimiya M, et al. Substance P-containing axon terminals in the mucosa of the human urinary bladder: pre-embedding immunohistochemistry using cryostat sections for electron microscopy. Histochemistry. 1993;100:401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

