[-2]Proenzyme prostate specific antigen is more accurate than total and free prostate specific antigen in differentiating prostate cancer from benign disease in a prospective prostate cancer screening study
- PMID: 20171670
- PMCID: PMC3537165
- DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.12.056
[-2]Proenzyme prostate specific antigen is more accurate than total and free prostate specific antigen in differentiating prostate cancer from benign disease in a prospective prostate cancer screening study
Abstract
Purpose: Due to the limited specificity of prostate specific antigen for prostate cancer screening, there is an ongoing search for adjunctive biomarkers. Retrospective studies have suggested that an isoform of proenzyme prostate specific antigen called [-2]proenzyme prostate specific antigen may enhance the specificity of prostate specific antigen based screening. We examined the usefulness of this isoform in a prospective prostate cancer screening study.
Materials and methods: From a population of 2,034 men undergoing prostate cancer screening we examined the relationship between the measurement of the [-2]isoform of proenzyme prostate specific antigen (p2PSA) and prostate cancer detection. Specifically we compared the usefulness of total prostate specific antigen, the ratio of free-to-total prostate specific antigen, the ratio of p2PSA-to-free prostate specific antigen, and a formula combining prostate specific antigen, free prostate specific antigen and p2PSA (the Beckman Coulter prostate health index or phi) to predict prostate cancer in men from the study undergoing prostate biopsy with a prostate specific antigen of 2.5 to 10 ng/ml and nonsuspicious digital rectal examination.
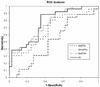
Results: Despite similar total prostate specific antigen (p = 0.88), percent free prostate specific antigen (p = 0.02) and %p2PSA (p = 0.0006) distinguished between positive and negative biopsy results. On ROC analysis %p2PSA (AUC 0.76) outperformed prostate specific antigen (AUC 0.50) and percent free prostate specific antigen (AUC 0.68) for differentiating between prostate cancer and benign disease. Setting the sensitivity at 88.5%, p2PSA led to a substantial improvement in specificity as well as positive and negative predictive values. The Beckman Coulter prostate health index (AUC 0.77) had the best overall performance characteristics.
Conclusions: This is the first prospective study to our knowledge to demonstrate that p2PSA provides improved discrimination between prostate cancer and benign disease in screened men with a prostate specific antigen of 2.5 to 10 ng/ml and a negative digital rectal examination.
Copyright (c) 2010 American Urological Association Education and Research, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Catalona WJ, Smith DS, Ratliff TL, et al. Measurement of prostate-specific antigen in serum as a screening test for prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:1156. - PubMed
-
- Tchetgen MB, Oesterling JE. The effect of prostatitis, urinary retention, ejaculation, and ambulation on the serum prostate-specific antigen concentration. Urol Clin North Am. 1997;24:283. - PubMed
-
- Emiliozzi P, Longhi S, Scarpone P, et al. The value of a single biopsy with 12 transperineal cores for detecting prostate cancer in patients with elevated prostate specific antigen. J Urol. 2001;166:845. - PubMed
-
- Okihara K, Fritsche HA, Ayala A, et al. Can complexed prostate specific antigen and prostatic volume enhance prostate cancer detection in men with total prostate specific antigen between 2.5 and 4.0 ng./ml. J Urol. 2001;165:1930. - PubMed
-
- Roehl KA, Antenor JA, Catalona WJ. Robustness of free prostate specific antigen measurements to reduce unnecessary biopsies in the 2.6 to 4.0 ng/ml range. J Urol. 2002;168:922. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical