Distribution of a novel binding site for angiotensins II and III in mouse tissues
- PMID: 20171994
- PMCID: PMC7114337
- DOI: 10.1016/j.regpep.2010.02.007
Distribution of a novel binding site for angiotensins II and III in mouse tissues
Abstract
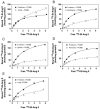
A novel binding site for angiotensins II and III that is unmasked by parachloromercuribenzoate has been reported in rat, mouse and human brains. Initial studies of this binding site indicate that it is not expressed in the adrenal, liver or kidney of the rat and mouse. To determine if this binding site occurs in other mouse tissues, 8 tissues were assayed for expression of this binding site by radioligand binding assay and compared with the expression of this binding site in the forebrain. Particulate fractions of homogenates of testis, epididymis, seminal vesicles, heart, spleen, pancreas, lung, skeletal muscle, and forebrain were incubated with (125)I-sarcosine(1), isoleucine(8) angiotensin II in the presence or absence of 0.3mM parachloromercuribenzoate plus 10microM losartan and 10microM PD123319 (to saturate AT(1) and AT(2) receptors). Specific (3microM angiotensin II displaceable) high affinity binding occurred in the testis>forebrain>epididymis>spleen>pancreas>lung when parachloromercuribenzoate was present. Binding could not be reliably observed in heart, skeletal muscle and seminal vesicles. High affinity binding of (125)I-sarcosine(1), isoleucine(8) angiotensin II was observed in the absence of parachloromercuribenzoate in the pancreas on occasion. This suggests that this novel angiotensin binding site may have a functional role in these tissues.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effects of para-chloromercuribenzoic acid and different oxidative and sulfhydryl agents on a novel, non-AT1, non-AT2 angiotensin binding site identified as neurolysin.Regul Pept. 2013 Jun 10;184:104-14. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2013.03.021. Epub 2013 Mar 16. Regul Pept. 2013. PMID: 23511333 Free PMC article.
-
Human brain contains a novel non-AT1, non-AT2 binding site for active angiotensin peptides.Life Sci. 2008 Sep 12;83(11-12):421-5. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2008.07.003. Epub 2008 Jul 22. Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18692076 Free PMC article.
-
Brain AT1 angiotensin receptor subtype binding: importance of peptidase inhibition for identification of angiotensin II as its endogenous ligand.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Oct;331(1):170-7. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.157461. Epub 2009 Jul 8. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009. PMID: 19587313
-
[Angiotensin II receptors in the adrenals].Probl Endokrinol (Mosk). 1980;26(6):74-83. Probl Endokrinol (Mosk). 1980. PMID: 6256730 Review. Russian. No abstract available.
-
Organisation and functional role of the brain angiotensin system.J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2002 Sep;3 Suppl 1:S39-48. doi: 10.3317/jraas.2002.029. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2002. PMID: 12428219 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Preliminary biochemical characterization of the novel, non-AT1, non-AT2 angiotensin binding site from the rat brain.Endocrine. 2010 Jun;37(3):442-8. doi: 10.1007/s12020-010-9328-2. Epub 2010 Apr 13. Endocrine. 2010. PMID: 20960166 Free PMC article.
-
AT₁ angiotensin II receptor and novel non-AT₁, non-AT₂ angiotensin II/III binding site in brainstem cardiovascular regulatory centers of the spontaneously hypertensive rat.Brain Res. 2010 Nov 4;1359:98-106. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.08.081. Epub 2010 Aug 31. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20807518 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Therapeutic Approaches Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin System and Associated Peptides in Hypertension and Heart Failure.Pharmacol Rev. 2019 Oct;71(4):539-570. doi: 10.1124/pr.118.017129. Pharmacol Rev. 2019. PMID: 31537750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass spectrometry for the molecular imaging of angiotensin metabolism in kidney.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Apr 15;302(8):E1016-24. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00515.2011. Epub 2012 Feb 7. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22318946 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of para-chloromercuribenzoic acid and different oxidative and sulfhydryl agents on a novel, non-AT1, non-AT2 angiotensin binding site identified as neurolysin.Regul Pept. 2013 Jun 10;184:104-14. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2013.03.021. Epub 2013 Mar 16. Regul Pept. 2013. PMID: 23511333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Phillips M.I., Speakman E.A., Kimura B. Levels of angiotensin and molecular biology of the tissue renin angiotensin systems. Regul Pept. 1993;43:1–20. - PubMed
-
- de Gasparo M., Catt K.J., Inagami T., Wright J.W., Unger T. International union of pharmacology. XXIII. The angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;52:415–472. - PubMed
-
- Thomas W.G., Mendelsohn F.A. Angiotensin receptors: form and function and distribution. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2003;35:774–779. - PubMed
-
- Phillips M.I., Sumners C. Angiotensin II in central nervous system physiology. Regul Pept. 1998;78:1–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

