A novel link to base excision repair?
- PMID: 20172733
- PMCID: PMC2866823
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2010.01.003
A novel link to base excision repair?
Abstract
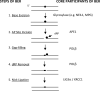
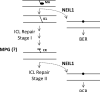
DNA interstrand crosslinks (ICLs) can arise from reactions with endogenous chemicals, such as malondialdehyde - a lipid peroxidation product - or from exposure to various clinical anti-cancer drugs, most notably bifunctional alkylators and platinum compounds. Because they covalently link the two strands of DNA, ICLs completely block transcription and replication, and, as a result, are lethal to the cell. It is well established that proteins that function in nucleotide excision repair and homologous recombination are involved in ICL resolution. Recent work, coupled with a much earlier report, now suggest an emerging link between proteins of the base excision repair pathway and crosslink processing.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
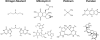

Similar articles
-
Involvement of nucleotide excision repair in a recombination-independent and error-prone pathway of DNA interstrand cross-link repair.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Feb;21(3):713-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.3.713-720.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11154259 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for base excision repair processing of DNA interstrand crosslinks.Mutat Res. 2013 Mar-Apr;743-744:44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2012.11.007. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Mutat Res. 2013. PMID: 23219605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in understanding the complex mechanisms of DNA interstrand cross-link repair.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Oct 1;5(10):a012732. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012732. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 24086043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleotide excision repair- and polymerase eta-mediated error-prone removal of mitomycin C interstrand cross-links.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jan;23(2):754-61. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.2.754-761.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12509472 Free PMC article.
-
DNA interstrand crosslinks induce a potent replication block followed by formation and repair of double strand breaks in intact mammalian cells.DNA Repair (Amst). 2012 Dec 1;11(12):976-85. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2012.09.010. Epub 2012 Oct 23. DNA Repair (Amst). 2012. PMID: 23099010
Cited by
-
APE1 polymorphic variants cause persistent genomic stress and affect cancer cell proliferation.Oncotarget. 2016 May 3;7(18):26293-306. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8477. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27050370 Free PMC article.
-
Novel role of base excision repair in mediating cisplatin cytotoxicity.J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 22;286(16):14564-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.225375. Epub 2011 Feb 28. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21357694 Free PMC article.
-
An inverse switch in DNA base excision and strand break repair contributes to melphalan resistance in multiple myeloma cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55493. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055493. Epub 2013 Feb 6. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23405159 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic cytotoxicity and DNA strand breaks in cells and plasmid DNA exposed to uranyl acetate and ultraviolet radiation.J Appl Toxicol. 2015 Apr;35(4):338-49. doi: 10.1002/jat.3015. Epub 2014 May 15. J Appl Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 24832689 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of APOBEC3B expression by chemotherapy drugs is mediated by DNA-PK-directed activation of NF-κB.Oncogene. 2021 Feb;40(6):1077-1090. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01583-7. Epub 2020 Dec 15. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33323971 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Summerfield FW, Tappel AL. Detection and measurement by high-performance liquid chromatography of malondialdehyde crosslinks in DNA. Anal. Biochem. 1984;143:265–271. - PubMed
-
- Kozekov ID, et al. Interchain cross-linking of DNA mediated by the principal adduct of acrolein. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001;14:1482–1485. - PubMed
-
- Cole RS. Light-induced cross-linking of DNA in the presence of a furocoumarin (psoralen). Studies with phage lambda, Escherichia coli, and mouse leukemia cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1970;217:30–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

