Use of the kinase inhibitor analog 1NM-PP1 reveals a role for Toxoplasma gondii CDPK1 in the invasion step
- PMID: 20173034
- PMCID: PMC2863409
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00351-09
Use of the kinase inhibitor analog 1NM-PP1 reveals a role for Toxoplasma gondii CDPK1 in the invasion step
Abstract
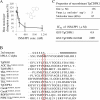
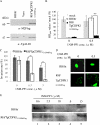
Toxoplasma gondii CDPK1 (TgCDPK1) was found to be the target of the toxoplasmocidal compound 1NM-PP1. When TgCDPK1 was mutated at position 128 from glycine to methionine, resistance was gained. Inhibition of gliding motility without inhibition of micronemal secretion by 1NM-PP1 suggests a function for TgCDPK1 in gliding motility.
Figures
References
-
- Bishop A. C., Ubersax J. A., Petsch D. T., Matheos D. P., Gray N. S., Blethrow J., Shimizu E., Tsien J. Z., Schultz P. G., Rose M. D., Wood J. L., Morgan D. O., Shokat K. M. 2000. A chemical switch for inhibitor-sensitive alleles of any protein kinase. Nature 407:395–401 - PubMed
-
- Carruthers V., Boothroyd J. C. 2007. Pulling together: an integrated model of Toxoplasma cell invasion. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 10:83–89 - PubMed
-
- Carruthers V. B., Giddings O. K., Sibley L. D. 1999. Secretion of micronemal proteins is associated with toxoplasma invasion of host cells. Cell. Microbiol. 1:225–235 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

