Interaction between activated chemokine receptor 1 and FcepsilonRI at membrane rafts promotes communication and F-actin-rich cytoneme extensions between mast cells
- PMID: 20173038
- PMCID: PMC2825160
- DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxp118
Interaction between activated chemokine receptor 1 and FcepsilonRI at membrane rafts promotes communication and F-actin-rich cytoneme extensions between mast cells
Abstract
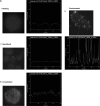
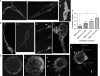
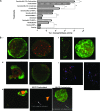
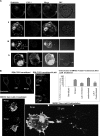
Chemokines play important regulatory roles in immunity, but their contributions to mast cell function remain poorly understood. We examined the effects of FcepsilonRI-chemokine receptor (CCR) 1 co-stimulation on receptor localization and cellular morphology of bone marrow-derived mast cells. Whereas FcepsilonRI and CCR1 co-localized at the plasma membrane in unsensitized cells, sensitization with IgE promoted internalization of CCR1 molecules. Co-stimulation of FcepsilonRI and CCR1 with antigen and macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha was more effective than FcepsilonRI stimulation alone in causing leading edge formation, flattened morphology, membrane ruffles and ganglioside (GM1(+)) lipid mediator release. Co-stimulation resulted in phalloidin-positive cytoneme-like cellular extensions, also known as tunneling nanotubes, which originated at points of calcium accumulation. This is the first report of cytoneme formation by mast cells. To determine the importance of lipid rafts for mast cell function, the cells were cholesterol depleted. Cholesterol depletion enhanced degranulation in resting, sensitized and co-stimulated cells, but not in FcepsilonRI-cross-linked cells, and inhibited formation of filamentous actin(+) cytonemes but not GM1(+) cytonemes. Treatment with latrunculin A to sequester globular-actin abolished cytoneme formation. The cytonemes may participate in intercellular communication during allergic and inflammatory responses, and their presence in the co-stimulated mast cells suggests new roles for CCRs in immunopathology.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Evidence that formation of vimentin mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) complex mediates mast cell activation following FcεRI/CC chemokine receptor 1 cross-talk.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 13;287(29):24516-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.319624. Epub 2012 May 21. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22613718 Free PMC article.
-
CCR1 expression and signal transduction by murine BMMC results in secretion of TNF-alpha, TGFbeta-1 and IL-6.Int Immunol. 2009 Aug;21(8):991-1001. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxp066. Epub 2009 Jul 10. Int Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19592420 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of genes and proteins specifically regulated by costimulation of mast cell Fcε Receptor I and chemokine receptor 1.Exp Mol Pathol. 2012 Jun;92(3):267-74. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2012.02.002. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Exp Mol Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22417871
-
Lipid rafts in mast cell signaling.Mol Immunol. 2002 Sep;38(16-18):1247-52. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(02)00071-8. Mol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12217391 Review.
-
A perspective: regulation of IgE receptor-mediated mast cell responses by a LAT-organized plasma membrane-localized signaling complex.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001 Jan-Mar;124(1-3):137-41. doi: 10.1159/000053692. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11306950 Review.
Cited by
-
ELAVL1 Role in Cell Fusion and Tunneling Membrane Nanotube Formations with Implication to Treat Glioma Heterogeneity.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 21;12(10):3069. doi: 10.3390/cancers12103069. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33096700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Communicating by touch--neurons are not alone.Trends Cell Biol. 2014 Jun;24(6):370-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2014.01.003. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Trends Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24560610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging role of contact-mediated cell communication in tissue development and diseases.Histochem Cell Biol. 2018 Nov;150(5):431-442. doi: 10.1007/s00418-018-1732-3. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 30255333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perivascular mast cells dynamically probe cutaneous blood vessels to capture immunoglobulin E.Immunity. 2013 Jan 24;38(1):166-75. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.09.022. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Immunity. 2013. PMID: 23290520 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered Nanostructures of Haptens Lead to Unexpected Formation of Membrane Nanotubes Connecting Rat Basophilic Leukemia Cells.ACS Nano. 2015 Jul 28;9(7):6738-46. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b02270. Epub 2015 Jun 18. ACS Nano. 2015. PMID: 26057701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kawakami T, Galli SJ. Regulation of mast-cell and basophil function and survival by IgE. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002;2:773. - PubMed
-
- Henz BM, Maurer M, Lippert U, Worm M, Babina M. Mast cells as initiators of immunity and host defense. Exp. Dermatol. 2001;10:1. - PubMed
-
- Taylor ML, Metcalfe DD. Mast cells in allergy and host defense. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2001;22:115. - PubMed
-
- Pulendran B, Ono SJ. A shot in the arm for mast cells. Nat. Med. 2008;14:489. - PubMed
-
- Metcalfe DD, Baram D, Mekori YA. Mast cells. Physiol. Rev. 1997;77:1033. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

