Toll-like receptor 2 mediates mesenchymal stem cell-associated myocardial recovery and VEGF production following acute ischemia-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 20173040
- PMCID: PMC2867442
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.01087.2009
Toll-like receptor 2 mediates mesenchymal stem cell-associated myocardial recovery and VEGF production following acute ischemia-reperfusion injury
Abstract
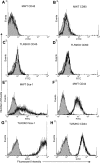
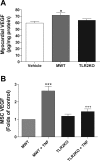
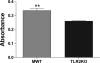
Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), a key component of the innate immune system, is linked to inflammation and myocardial dysfunction after ischemia-reperfusion injury (I/R). Treatment of the heart with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) is known to improve myocardial recovery after I/R in part by paracrine factors such as VEGF. However, it is unknown whether TLR2 activation on the MSCs affects MSC-mediated myocardial recovery and VEGF production. We hypothesized that the knockout of TLR2 on the MSCs (TLR2KO MSCs) would 1) improve MSC-mediated myocardial recovery and 2) increase myocardial and MSC VEGF release. With the isolated heart perfusion system, Sprague-Dawley rat hearts were subjected to I/R and received one of three intracoronary treatments: vehicle, male wild-type MSCs (MWT MSCs), or TL2KO MSCs. All treatments were performed immediately before ischemia, and heart function was measured continuously. Postreperfusion, heart homogenates were analyzed for myocardial VEGF production. Contrary to our hypothesis, only MWT MSC treatment significantly improved the recovery of left ventricular developed pressure and the maximal positive and negative values of the first derivative of pressure. In addition, VEGF production was greatest in hearts treated with MWT MSCs. To investigate MSC production of VEGF, MSCs were activated with TNF in vitro and the supernatants collected for ELISA. In vitro basal levels of MSC VEGF production were similar. However, with TNF activation, MWT MSCs produced significantly more VEGF, whereas activated TLR2KO MSC production of VEGF was unchanged. Finally, we observed that MWT MSCs proliferated more rapidly than TLR2KO MSCs. These data indicate that TLR2 may be essential to MSC-mediated myocardial recovery and VEGF production.
Figures

References
-
- Abarbanell AM, Coffey AC, Fehrenbacher JW, Beckman DJ, Herrmann JL, Weil B, Meldrum DR. Proinflammatory cytokine effects on mesenchymal stem cell therapy for the ischemic heart. Ann Thorac Surg 88: 1036–1043, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Addya S, Shiroto K, Turoczi T, Zhan L, Kaga S, Fukuda S, Surrey S, Duan LJ, Fong GH, Yamamoto F, Maulik N. Ischemic preconditioning-mediated cardioprotection is disrupted in heterozygous Flt-1 (VEGFR-1) knockout mice. J Mol Cell Cardiol 38: 345–351, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Askari A, Unzek S, Goldman CK, Ellis SG, Thomas JD, DiCorleto PE, Topol EJ, Penn MS. Cellular, but not direct, adenoviral delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor results in improved left ventricular function and neovascularization in dilated ischemic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 43: 1908–1914, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Atoui R, Shum-Tim D, Chiu RC. Myocardial regenerative therapy: immunologic basis for the potential “universal donor cells”. Ann Thorac Surg 86: 327–334, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Baddoo M, Hill K, Wilkinson R, Gaupp D, Hughes C, Kopen GC, Phinney DG. Characterization of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from murine bone marrow by negative selection. J Cell Biochem 89: 1235–1249, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

