Sex-related resistance to myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury is associated with high constitutive ARC expression
- PMID: 20173041
- PMCID: PMC2867440
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.01021.2009
Sex-related resistance to myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury is associated with high constitutive ARC expression
Abstract
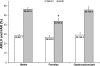
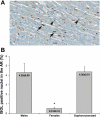
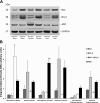
The female sex has been associated with improved myocardial salvage after ischemia and reperfusion (I/R). Estrogen, specifically 17beta-estradiol, has been demonstrated to mediate this phenomenon by limiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis. We sought to quantitatively assess the effect of sex, ovarian hormone loss, and I/R on myocardial Bax, Bcl-2, and apoptosis repressor with caspase recruitment domain (ARC) expression. Male (n = 48), female (n = 26), and oophorectomized female (n = 20) rabbits underwent 30 min of regional ischemia and 3 h of reperfusion. The myocardial area at risk and infarct size were determined using a double-staining technique and planimetry. In situ oligo ligation was used to assess apoptotic cell death. Western blot analysis was used to determine proapoptotic (Bax) and antiapoptotic (Bcl-2 and ARC) protein levels in all three ischemic groups and, additionally, in three nonischemic groups. Infarct size (43.7 +/- 3.2%) and apoptotic cell death (0.51 +/- 0.10%) were significantly attenuated in females compared with males (56.4 +/- 1.6%, P < 0.01, and 4.29 +/- 0.95%, P < 0.01) and oophorectomized females (55.7 +/- 3.4%, P < 0.05, and 4.36 +/- 0.51%, P < 0.01). Females expressed significantly higher baseline ARC levels (3.62 +/- 0.29) compared with males (1.78 +/- 0.18, P < 0.01) and oophorectomized females (1.08 +/- 0.26, P < 0.01). Males expressed a significantly higher baseline Bax-to-Bcl-2 ratio (4.32 +/- 0.99) compared with females (0.65 +/- 0.13, P < 0.01) and oophorectomized females (0.42 +/- 0.10, P < 0.01). I/R significantly reduced Bax-to-Bcl-2 ratios in males. In all other groups, ARC levels and Bax-to-Bcl-2 ratios did not significantly change. These results support the conclusion that in females, endogenous estrogen limits I/R-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by producing a baseline antiapoptotic profile, which is associated with estrogen-dependent high constitutive myocardial ARC expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The protective effect of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist on postischemic reperfused myocardium and its possible mechanism].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004 Apr 2;84(7):548-53. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15144587 Chinese.
-
Effects of ACE inhibition on myocardial apoptosis in an ischemia-reperfusion rat heart model.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2003 Jun;41(6):880-9. doi: 10.1097/00005344-200306000-00008. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12775965
-
Adenosine attenuates reperfusion-induced apoptotic cell death by modulating expression of Bcl-2 and Bax proteins.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001 Jan;33(1):57-68. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.2000.1275. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001. PMID: 11133223
-
Influences of remifentanil on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and the expressions of Bax and Bcl-2 in rats.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Dec;22(24):8951-8960. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201812_16665. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30575939
-
A double-edged sword: role of apoptosis repressor with caspase recruitment domain (ARC) in tumorigenesis and ischaemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury.Apoptosis. 2023 Apr;28(3-4):313-325. doi: 10.1007/s10495-022-01802-4. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Apoptosis. 2023. PMID: 36652128 Review.
Cited by
-
Sex Differences in Therapies against Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: From Basic Science to Clinical Perspectives.Cells. 2023 Aug 16;12(16):2077. doi: 10.3390/cells12162077. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37626887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of apoptosis repressor with caspase recruitment domain (ARC) in cell death and cardiovascular disease.Apoptosis. 2021 Feb;26(1-2):24-37. doi: 10.1007/s10495-020-01653-x. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Apoptosis. 2021. PMID: 33604728 Review.
-
Autophagy Regulatory Network - a systems-level bioinformatics resource for studying the mechanism and regulation of autophagy.Autophagy. 2015;11(1):155-65. doi: 10.4161/15548627.2014.994346. Autophagy. 2015. PMID: 25635527 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Snord116 protects cardiomyocyte kinetics during ischemic stress.J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2025 Mar 2;11:100291. doi: 10.1016/j.jmccpl.2025.100291. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2025. PMID: 40124788 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-based differences in cardiac ischaemic injury and protection: therapeutic implications.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Feb;171(3):541-54. doi: 10.1111/bph.12270. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 23750471 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bae S, Zhang L. Gender differences in cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion injury in adult rat hearts: focus on Akt and protein kinase C signaling. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315: 1125–1135, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Booth EA, Marchesi M, Kilbourne EJ, Lucchesi BR. 17β-Estradiol as a receptor-mediated cardioprotective agent. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307: 395–401, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Booth EA, Marchesi M, Knittel AK, Kilbourne EJ, Lucchesi BR. The pathway-selective estrogen receptor ligand WAY-169916 reduces infarct size after myocardial ischemia and reperfusion by an estrogen receptor dependent mechanism. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 49: 401–407, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Das B, Sarkar C. Similarities between ischemic preconditioning and 17β-estradiol mediated cardiomyocyte KATP channel activation leading to cardioprotective and antiarrhythmic effects during ischemia/reperfusion in the intact rabbit heart. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 47: 277–286, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Eefting F, Rensing B, Wigman J, Pannekoek WJ, Liu WM, Cramer MJ, Lips DJ, Doevendans PA. Role of apoptosis in reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res 61: 414–426, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

