Mice deficient in Mkp-1 develop more severe pulmonary hypertension and greater lung protein levels of arginase in response to chronic hypoxia
- PMID: 20173047
- PMCID: PMC2867445
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00813.2009
Mice deficient in Mkp-1 develop more severe pulmonary hypertension and greater lung protein levels of arginase in response to chronic hypoxia
Abstract
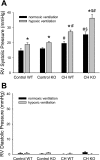
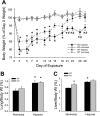
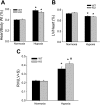
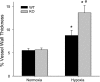
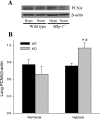
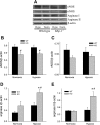
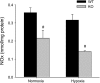
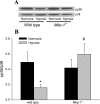
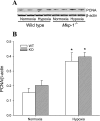
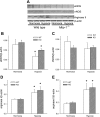
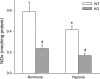
The mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases are involved in cellular responses to many stimuli, including hypoxia. MAP kinase signaling is regulated by a family of phosphatases that include MAP kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1). We hypothesized that mice lacking the Mkp-1 gene would have exaggerated chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Wild-type (WT) and Mkp-1(-/-) mice were exposed to either 4 wk of normoxia or hypobaric hypoxia. Following chronic hypoxia, both genotypes demonstrated elevated right ventricular pressures, right ventricular hypertrophy as demonstrated by the ratio of the right ventricle to the left ventricle plus septum weights [RV(LV + S)], and greater vascular remodeling. However, the right ventricular systolic pressures, the RV/(LV + S), and the medial wall thickness of 100- to 300-microm vessels was significantly greater in the Mkp-1(-/-) mice than in the WT mice following 4 wk of hypobaric hypoxia. Chronic hypoxic exposure caused no detectable change in eNOS protein levels in the lungs in either genotype; however, Mkp-1(-/-) mice had lower levels of eNOS protein and lower lung NO production than did WT mice. No iNOS protein was detected in the lungs by Western blotting in any condition in either genotype. Both arginase I and arginase II protein levels were greater in the lungs of hypoxic Mkp-1(-/-) mice than those in hypoxic WT mice. Lung levels of proliferating cell nuclear antigen were greater in hypoxic Mkp-1(-/-) than in hypoxic WT mice. These data are consistent with the concept that MKP-1 acts to restrain hypoxia-induced arginase expression and thereby reduces vascular remodeling and the severity of pulmonary hypertension.
Figures
References
-
- Albina JE, Mahoney EJ, Daley JM, Wesche DE, Morris SM, Jr, Reichner JS. Macrophage arginase regulation by CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta. Shock 23: 168–72, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Bueno OF, De Windt LJ, Lim HW, Tymitz KM, Witt SA, Kimball TR, Molkentin JD. The dual-specificity phosphatase MKP-1 limits the cardiac hypertrophic response in vitro and in vivo. Circ Res 88: 88–96, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Buermans HPJ, Redout EM, Schiel AE, Musters RJP, Zuidwijk M, Eijk PP, van Hardeveld C, Kasanmoentalib S, Visser FC, Ylstra B, Simonides WS. Microarray analysis reveals pivotal divergent mRNA expression profiles early in the development of either compensated ventricular hypertrophy or heart failure. Physiol Genomics 21: 314–323, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Case D, Irwin D, Ivester C, Harral J, Morris K, Imamura M, Roedersheimer M, Paterson A, Carr M, Hagen M, Saavedra M, Crossno J, Young KA, Dempsey EC, Poirier F, West J, Majka S. Mice deficient in galectin-1 exhibit attenuated physiological responses to chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 292: L154–L164, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Calvert TJ, Chicoine LG, Liu Y, Nelin LD. Deficiency of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphotase-1 results in iNOS-mediated hypotension in response to low-dose endotoxin. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294: H1621–H1629, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

