miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin and cancer metastasis
- PMID: 20173740
- PMCID: PMC2845545
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb2024
miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin and cancer metastasis
Abstract
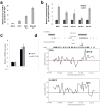
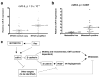
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are increasingly implicated in regulating the malignant progression of cancer. Here we show that miR-9, which is upregulated in breast cancer cells, directly targets CDH1, the E-cadherin-encoding messenger RNA, leading to increased cell motility and invasiveness. miR-9-mediated E-cadherin downregulation results in the activation of beta-catenin signalling, which contributes to upregulated expression of the gene encoding vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF); this leads, in turn, to increased tumour angiogenesis. Overexpression of miR-9 in otherwise non-metastatic breast tumour cells enables these cells to form pulmonary micrometastases in mice. Conversely, inhibiting miR-9 by using a 'miRNA sponge' in highly malignant cells inhibits metastasis formation. Expression of miR-9 is activated by MYC and MYCN, both of which directly bind to the mir-9-3 locus. Significantly, in human cancers, miR-9 levels correlate with MYCN amplification, tumour grade and metastatic status. These findings uncover a regulatory and signalling pathway involving a metastasis-promoting miRNA that is predicted to directly target expression of the key metastasis-suppressing protein E-cadherin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
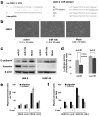
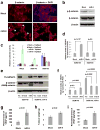
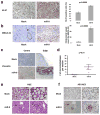
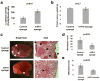
Comment in
-
Myc-modulated miR-9 makes more metastases.Nat Cell Biol. 2010 Mar;12(3):209-11. doi: 10.1038/ncb0310-209. Epub 2010 Feb 21. Nat Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20173743
References
-
- Fidler IJ. The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:453–8. - PubMed
-
- Thiery JP. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:442–54. - PubMed
-
- Nicoloso MS, Spizzo R, Shimizu M, Rossi S, Calin GA. MicroRNAs--the micro steering wheel of tumour metastases. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:293–302. - PubMed
-
- Ma L, Weinberg RA. Micromanagers of malignancy: role of microRNAs in regulating metastasis. Trends Genet. 2008;24:448–56. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

