Two-photon uncaging of gamma-aminobutyric acid in intact brain tissue
- PMID: 20173751
- PMCID: PMC4104925
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.321
Two-photon uncaging of gamma-aminobutyric acid in intact brain tissue
Abstract
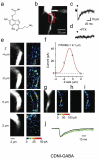
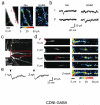
We have synthesized a photosensitive (or caged) 4-carboxymethoxy-5,7-dinitroindolinyl (CDNI) derivative of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Two-photon excitation of CDNI-GABA produced rapid activation of GABAergic currents in neurons in brain slices with an axial resolution of approximately 2 mum and enabled high-resolution functional mapping of GABA-A receptors. Two-photon uncaging of GABA, the main inhibitory neurotransmitter, should allow detailed studies of receptor function and synaptic integration with subcellular precision.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

