Insulin therapy stimulates lipid synthesis and improves endocrine functions of adipocytes in dietary obese C57BL/6 mice
- PMID: 20173758
- PMCID: PMC4002414
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2010.17
Insulin therapy stimulates lipid synthesis and improves endocrine functions of adipocytes in dietary obese C57BL/6 mice
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate whether insulin intervention could affect the metabolic and endocrine functions of adipose tissue.
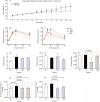
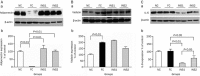
Methods: C57BL/6 mice were fed on a high-fat-diet for 12-16 weeks to induce insulin resistance. Insulin intervention was administered in the high-fat-diet mice for 4 weeks at 12 weeks (early insulin treatment) or 16 weeks (late insulin treatment). Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance tests were performed before and after insulin treatment. Expression levels of factors involved in the triglyceride synthesis and endocrine functions of adipose tissue including phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK-C), fatty acid synthase (FAS), aquaporin 7 (AQP7), adiponectin, visfatin, and interleukin-6 (IL-6) were determined by Western blot.
Results: In the obese mice, glucose tolerance was impaired; triglyceride content was increased in the liver tissue; protein expression of FAS and adiponectin was decreased; expression of visfatin was increased in adipose tissue. After 4-week insulin treatment, glucose tolerance was improved; triglyceride content was decreased in the liver and skeletal muscle; expression of PEPCK-C, FAS, and adiponectin was increased in the adipose tissue; IL-6 and AQP7 expression was reduced in the fat. Early insulin treatment had better effect in increasing the expression of FAS and PEPCK-C and decreasing the expression of IL-6.
Conclusion: These results indicate that insulin can target adipocytes for improvement of insulin sensitivity through stimulating triglyceride synthesis and partly improving endocrine functions.
Figures

References
-
- Weng J, Li Y, Xu W, Shi L, Zhang Q, Zhu D, et al. Effect of intensive insulin therapy on beta-cell function and glycaemic control in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a multicentre randomised parallel-group trial. Lancet. 2008;371:1753–60. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Xu W, Liao Z, Yao B, Chen X, Huang Z, et al. Induction of long-term glycemic control in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients is associated with improvement of beta-cell function. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:2597–602. - PubMed
-
- Ryan EA, Imes S, Wallace C. Short-term intensive insulin therapy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1028–32. - PubMed
-
- Matthaei S, Stumvoll M, Kellerer M, Haring HU. Pathophysiology and pharmacological treatment of insulin resistance. Endocr Rev. 2000;21:585–618. - PubMed
-
- Tordjman J, Chauvet G, Quette J, Beale EG, Forest C, Antoine B. Thiazolidinediones block fatty acid release by inducing glycero-neogenesis in fat cells. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:18785–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

