Targeting the FANCJ-BRCA1 interaction promotes a switch from recombination to poleta-dependent bypass
- PMID: 20173781
- PMCID: PMC2909592
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.18
Targeting the FANCJ-BRCA1 interaction promotes a switch from recombination to poleta-dependent bypass
Abstract
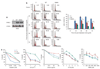
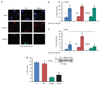
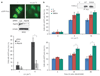
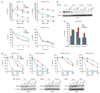
BRCA1 and the DNA helicase FANCJ (also known as BACH1 or BRIP1) have common functions in breast cancer suppression and DNA repair. However, the functional significance of the direct interaction between BRCA1 and FANCJ remains unclear. Here, we have discovered that BRCA1 binding to FANCJ regulates DNA damage repair choice. Thus, when FANCJ binding to BRCA1 is ablated, the molecular mechanism chosen for the repair of damaged DNA is dramatically altered. Specifically, a FANCJ protein that cannot be phosphorylated at serine 990 or bind BRCA1 inhibits DNA repair via homologous recombination and promotes poleta-dependent bypass. Furthermore, the poleta-dependent bypass promoted by FANCJ requires the direct binding to the mismatch repair (MMR) protein, MLH1. Together, our findings implicate that in human cells BRCA1 binding to FANCJ is critical to regulate DNA repair choice and promote genomic stability. Moreover, unregulated FANCJ function could be associated with cancer and/or chemoresistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Albertella MR, Green CM, Lehmann AR, O’Connor MJ. A role for polymerase eta in the cellular tolerance to cisplatin-induced damage. Cancer Res. 2005;65:9799–9806. - PubMed
-
- Alt A, Lammens K, Chiocchini C, Lammens A, Pieck JC, Kuch D, et al. Bypass of DNA lesions generated during anticancer treatment with cisplatin by DNA polymerase eta. Science. 2007;318:967–970. - PubMed
-
- Barbour L, Xiao W. Regulation of alternative replication bypass pathways at stalled replication forks and its effects on genome stability: a yeast model. Mutat Res. 2003;532:137–155. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya A, Ear US, Koller BH, Weichselbaum RR, Bishop DK. The breast cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1 is required for subnuclear assembly of Rad51 and survival following treatment with the DNA cross-linking agent cisplatin. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:23899–23903. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

