A role for S1P and S1P1 in immature-B cell egress from mouse bone marrow
- PMID: 20174580
- PMCID: PMC2823786
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009277
A role for S1P and S1P1 in immature-B cell egress from mouse bone marrow
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2010;5(3). doi: 10.1371/annotation/2ae645ec-9413-4f7d-b51f-eb0678fa2f1b
Abstract
B lymphocyte egress from secondary lymphoid organs requires sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) and S1P receptor-1 (S1P1). However, whether S1P contributes to immature-B cell egress from the bone marrow (BM) has not been fully assessed. Here we report that in S1P- and S1P1-conditionally deficient mice, the number of immature-B cells in the BM parenchyma increased, while it decreased in the blood. Moreover, a slower rate of bromodeoxyuridine incorporation suggested immature-B cells spent longer in the BM of mice in which S1P1-S1P signaling was genetically or pharmacologically impaired. Transgenic expression of S1P1 in developing B cells was sufficient to mobilize pro- and pre-B cells from the BM. We conclude that the S1P1-S1P pathway contributes to egress of immature-B cells from BM, and that this mechanism is partially redundant with other undefined pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
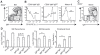
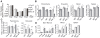
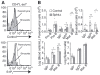
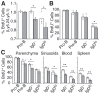
References
-
- Osmond DG, Batten SJ. Genesis of B lymphocytes in the bone marrow: extravascular and intravascular localization of surface IgM-bearing cells in mouse bone marrow detected by electron-microscope radioautography after in vivo perfusion of 125I anti-IgM antibody. Am J Anat. 1984;170:349–365. - PubMed
-
- Batten SJ, Osmond DG. The localization of B lymphocytes in mouse bone marrow: radioautographic studies after in vivo perfusion of radiolabelled anti-IgM antibody. J Immunol Methods. 1984;72:381–399. - PubMed
-
- Pappu R, Schwab SR, Cornelissen I, Pereira JP, Regard JB, et al. Promotion of lymphocyte egress into blood and lymph by distinct sources of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Science. 2007;316:295–298. - PubMed
-
- Schwab SR, Pereira JP, Matloubian M, Xu Y, Huang Y, et al. Lymphocyte sequestration through S1P lyase inhibition and disruption of S1P gradients. Science. 2005;309:1735–1739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

