Skeletal muscle phenotypically converts and selectively inhibits metastatic cells in mice
- PMID: 20174581
- PMCID: PMC2823787
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009299
Skeletal muscle phenotypically converts and selectively inhibits metastatic cells in mice
Abstract
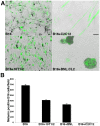
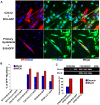
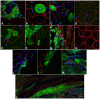
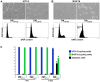
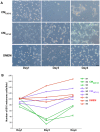
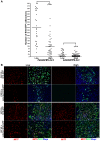
Skeletal muscle is rarely a site of malignant metastasis; the molecular and cellular basis for this rarity is not understood. We report that myogenic cells exert pronounced effects upon co-culture with metastatic melanoma (B16-F10) or carcinoma (LLC1) cells including conversion to the myogenic lineage in vitro and in vivo, as well as inhibition of melanin production in melanoma cells coupled with cytotoxic and cytostatic effects. No effect is seen with non-tumorigenic cells. Tumor suppression assays reveal that the muscle-mediated tumor suppressor effects do not generate resistant clones but function through the down-regulation of the transcription factor MiTF, a master regulator of melanocyte development and a melanoma oncogene. Our findings point to skeletal muscle as a source of therapeutic agents in the treatment of metastatic cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Fidler IJ. Critical determinants of cancer metastasis: rationale for therapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1999;43(Suppl):S3–10. - PubMed
-
- Greig RG, Trainer DL. Shaping future strategies for the pharmacological control of tumor cell metastases. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1986;5:3–14. - PubMed
-
- Klein CA. The direct molecular analysis of metastatic precursor cells in breast cancer: A chance for a better understanding of metastasis and for personalised medicine. Eur J Cancer 2008 - PubMed
-
- Langley RR, Fidler IJ. Tumor cell-organ microenvironment interactions in the pathogenesis of cancer metastasis. Endocr Rev. 2007;28:297–321. - PubMed
-
- Crissman JD. Tumor-host interactions as prognostic factors in the histologic assessment of carcinomas. Pathol Annu. 1986;21 Pt 1:29–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

