Fibroblasts express immune relevant genes and are important sentinel cells during tissue damage in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)
- PMID: 20174584
- PMCID: PMC2823790
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009304
Fibroblasts express immune relevant genes and are important sentinel cells during tissue damage in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)
Abstract
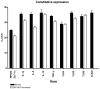
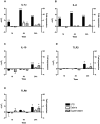
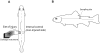
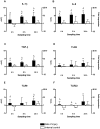
Fibroblasts have shown to be an immune competent cell type in mammals. However, little is known about the immunological functions of this cell-type in lower vertebrates. A rainbow trout hypodermal fibroblast cell-line (RTHDF) was shown to be responsive to PAMPs and DAMPs after stimulation with LPS from E. coli, supernatant and debris from sonicated RTHDF cells. LPS was overall the strongest inducer of IL-1beta, IL-8, IL-10, TLR-3 and TLR-9. IL-1beta and IL-8 were already highly up regulated after 1 hour of LPS stimulation. Supernatant stimuli significantly increased the expression of IL-1beta, TLR-3 and TLR-9, whereas the debris stimuli only increased expression of IL-1beta. Consequently, an in vivo experiment was further set up. By mechanically damaging the muscle tissue of rainbow trout, it was shown that fibroblasts in the muscle tissue of rainbow trout contribute to electing a highly local inflammatory response following tissue injury. The damaged muscle tissue showed a strong increase in the expression of the immune genes IL-1beta, IL-8 and TGF-beta already 4 hours post injury at the site of injury while the expression in non-damaged muscle tissue was not influenced. A weaker, but significant response was also seen for TLR-9 and TLR-22. Rainbow trout fibroblasts were found to be highly immune competent with a significant ability to express cytokines and immune receptors. Thus fish fibroblasts are believed to contribute significantly to local inflammatory reactions in concert with the traditional immune cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inflammatory and regenerative responses in salmonids following mechanical tissue damage and natural infection.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010 Sep;29(3):440-50. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2010.05.002. Epub 2010 May 21. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20472069
-
Fish cell cultures as in vitro models of inflammatory responses elicited by immunostimulants. Expression of regulatory genes of the innate immune response.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013 Sep;35(3):979-87. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2013.07.015. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23872473
-
Identification and expression analysis of two interleukin-23α (p19) isoforms, in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss and Atlantic salmon Salmo salar.Mol Immunol. 2015 Aug;66(2):216-28. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.03.014. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25841173
-
Peptidoglycan, not endotoxin, is the key mediator of cytokine gene expression induced in rainbow trout macrophages by crude LPS.Mol Immunol. 2010 Apr;47(7-8):1450-7. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2010.02.009. Epub 2010 Mar 20. Mol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20304498
-
Immune effects observed after the injection of plasmids coding for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) CK5B, CK6 and CK7A chemokines demonstrate their immunomodulatory capacity and reveal CK6 as a major interferon inducer.Dev Comp Immunol. 2009 Oct;33(10):1137-45. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2009.06.008. Epub 2009 Jun 27. Dev Comp Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19539644
Cited by
-
Toll-like receptor signaling in teleosts.Sci China Life Sci. 2025 Jul;68(7):1889-1911. doi: 10.1007/s11427-024-2822-5. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Sci China Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39961973 Review.
-
Cartilage Acidic Protein a Novel Therapeutic Factor to Improve Skin Damage Repair?Mar Drugs. 2021 Sep 25;19(10):541. doi: 10.3390/md19100541. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34677440 Free PMC article.
-
Transport Stress Induces Skin Innate Immunity Response in Hybrid Yellow Catfish (Tachysurus fulvidraco♀ × P. vachellii♂) Through TLR/NLR Signaling Pathways and Regulation of Mucus Secretion.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 12;12:740359. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.740359. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34712228 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factor GLI1 modulates the inflammatory response during pancreatic tissue remodeling.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 3;289(40):27727-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.556563. Epub 2014 Aug 7. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25104358 Free PMC article.
-
Improving a fish intestinal barrier model by combining two rainbow trout cell lines: epithelial RTgutGC and fibroblastic RTgutF.Cytotechnology. 2019 Aug 1;71(4):835-848. doi: 10.1007/s10616-019-00327-0. Epub 2019 Jun 29. Cytotechnology. 2019. PMID: 31256301 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaiser P, Rothwell L, Avery S, Balu S. Evolution of the interleukins. Developmental and Comparative Immunology. 2004;28:375–394. - PubMed
-
- Martin P, Leibovich SJ. Inflammatory cells during wound repair: the good, the bad and the ugly. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15:599–607. - PubMed
-
- Magor BG, Magor KE. Evolution of effectors and receptors of innate immunity. Developmental and Comparative Immunology. 2001;25:651–682. - PubMed
-
- Sepulcre MP, Alcaraz-Perez F, Lopez-Munoz A, Roca FJ, Meseguer J, et al. Evolution of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Recognition and Signaling: Fish TLR4 Does Not Recognize LPS and Negatively Regulates NF-kB Activation. J Immunol. 2009;182:1836–1845. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

