Nuclear entry of activated MAPK is restricted in primary ovarian and mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 20174585
- PMCID: PMC2823791
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009295
Nuclear entry of activated MAPK is restricted in primary ovarian and mammary epithelial cells
Abstract
Background: The MAPK/ERK1/2 serine kinases are primary mediators of the Ras mitogenic signaling pathway. Phosphorylation by MEK activates MAPK/ERK in the cytoplasm, and phospho-ERK is thought to enter the nucleus readily to modulate transcription.
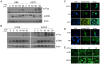
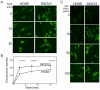
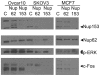
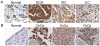
Principal findings: Here, however, we observe that in primary cultures of breast and ovarian epithelial cells, phosphorylation and activation of ERK1/2 are disassociated from nuclear translocalization and transcription of downstream targets, such as c-Fos, suggesting that nuclear translocation is limited in primary cells. Accordingly, in import assays in vitro, primary cells showed a lower import activity for ERK1/2 than cancer cells, in which activated MAPK readily translocated into the nucleus and activated c-Fos expression. Primary cells express lower levels of nuclear pore complex proteins and the nuclear transport factors, importin B1 and importin 7, which may explain the limiting ERK1/2 import found in primary cells. Additionally, reduction in expression of nucleoporin 153 by siRNA targeting reduced ERK1/2 nuclear activity in cancer cells.
Conclusion: ERK1/2 activation is dissociated from nuclear entry, which is a rate limiting step in primary cells and in vivo, and the restriction of nuclear entry is disrupted in transformed cells by the increased expression of nuclear pores and/or nuclear transport factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stimulus-coupled spatial restriction of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 activity contributes to the specificity of signal-response pathways.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Dec;24(23):10145-50. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.23.10145-10150.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15542825 Free PMC article.
-
Cigarette smoke exposure reveals a novel role for the MEK/ERK1/2 MAPK pathway in regulation of CFTR.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jun;1850(6):1224-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.02.004. Epub 2015 Feb 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25697727 Free PMC article.
-
Novel signaling molecules implicated in tumor-associated fatty acid synthase-dependent breast cancer cell proliferation and survival: Role of exogenous dietary fatty acids, p53-p21WAF1/CIP1, ERK1/2 MAPK, p27KIP1, BRCA1, and NF-kappaB.Int J Oncol. 2004 Mar;24(3):591-608. Int J Oncol. 2004. PMID: 14767544
-
Nuclear extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 translocation is mediated by casein kinase 2 and accelerated by autophosphorylation.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Sep;31(17):3515-30. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05424-11. Epub 2011 Jul 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. Retraction in: Mol Cell Biol. 2018 May 15;38(11):e00106-18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00106-18. PMID: 21730285 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Key signalling nodes in mammary gland development and cancer. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling in experimental models of breast cancer progression and in mammary gland development.Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(5):209. doi: 10.1186/bcr2361. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19818165 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The nuclear lamina regulates germline stem cell niche organization via modulation of EGFR signaling.Cell Stem Cell. 2013 Jul 3;13(1):73-86. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2013.05.003. Cell Stem Cell. 2013. PMID: 23827710 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting colorectal cancer at the level of nuclear pore complex.J Adv Res. 2025 Apr;70:423-444. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.06.009. Epub 2024 Jun 13. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38876192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importin β1 regulates cell growth and survival during adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma therapy.Invest New Drugs. 2021 Apr;39(2):317-329. doi: 10.1007/s10637-020-01007-z. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Invest New Drugs. 2021. PMID: 32959166
-
Casein kinase 2 sends extracellular signal-regulated kinase nuclear.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Sep;31(17):3512-4. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05916-11. Epub 2011 Jul 26. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21791609 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
PTN signaling: Components and mechanistic insights in human ovarian cancer.Mol Carcinog. 2015 Dec;54(12):1772-85. doi: 10.1002/mc.22249. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Mol Carcinog. 2015. PMID: 25418856 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gille H, Sharrocks AD, Shaw PE. Phosphorylation of transcription factor p62TCF by MAP kinase stimulates ternary complex formation at c-fos promoter. Nature. 1992;359:414–424. - PubMed
-
- Marais R, Wynne J, Treisman R. The SRF accessory protein Elk-1 contains a growth factor-regulated transcriptional activation domain. Cell. 1993;65:663–675. - PubMed
-
- Corson LB, Yamanaka Y, Lai K-MV, Rossant J. Spatial and temporal patterns of ERK signaling during mouse embryogenesis. Development. 2003;130:4527–4537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

