Overexpression of the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP3 regulates XA21-mediated innate immunity in rice
- PMID: 20174657
- PMCID: PMC2822859
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009262
Overexpression of the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP3 regulates XA21-mediated innate immunity in rice
Abstract
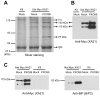
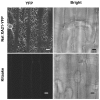
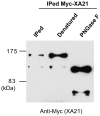
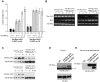
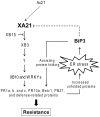
Recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) activates the innate immune response. Although PRR-mediated signaling events are critical to the survival of plants and animals, secretion and localization of PRRs have not yet been clearly elucidated. Here we report the in vivo interaction of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperone BiP3 with the rice XA21 PRR, which confers resistance to the Gram negative bacterium, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo). We show that XA21 is glycosylated and is primarily localized to the ER and also to the plasma membrane (PM). In BiP3-overexpressing rice plants, XA21-mediated immunity is compromised, XA21 stability is significantly decreased, and XA21 proteolytic cleavage is inhibited. BiP3 overexpression does not affect the general rice defense response, cell death or brassinolide-induced responses. These results indicate that BiP3 regulates XA21 protein stability and processing and that this regulation is critical for resistance to Xoo.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
The endoplasmic reticulum-quality control component SDF2 is essential for XA21-mediated immunity in rice.Plant Sci. 2013 Sep;210:53-60. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 May 14. Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 23849113
-
Rice BiP3 regulates immunity mediated by the PRRs XA3 and XA21 but not immunity mediated by the NB-LRR protein, Pi5.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 May 23;448(1):70-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.04.093. Epub 2014 Apr 26. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24780396
-
Paladin, a tyrosine phosphatase-like protein, is required for XA21-mediated immunity in rice.Plant Commun. 2021 Jun 29;2(4):100215. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2021.100215. eCollection 2021 Jul 12. Plant Commun. 2021. PMID: 34327325 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidation of XA21-mediated innate immunity.Cell Microbiol. 2010 Aug;12(8):1017-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2010.01489.x. Epub 2010 Jun 25. Cell Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20590657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Advances of rice bacterial blight disease resistance gene Xa21].Yi Chuan. 2006 Jun;28(6):745-53. Yi Chuan. 2006. PMID: 16818441 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
A model for the biosynthesis and transport of plasma membrane-associated signaling receptors to the cell surface.Front Plant Sci. 2012 Apr 13;3:71. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00071. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22639660 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-like kinase complexes in plant innate immunity.Front Plant Sci. 2012 Aug 24;3:209. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00209. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22936944 Free PMC article.
-
OsWRKY67 Plays a Positive Role in Basal and XA21-Mediated Resistance in Rice.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Jan 11;8:2220. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.02220. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29375598 Free PMC article.
-
Heat Shock Proteins: A Review of the Molecular Chaperones for Plant Immunity.Plant Pathol J. 2015 Dec;31(4):323-33. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.RW.08.2015.0150. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Plant Pathol J. 2015. PMID: 26676169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Class II small heat shock protein OsHsp18.0 plays positive roles in both biotic and abiotic defense responses in rice.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 12;7(1):11333. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11882-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28900229 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

