Nutlin-3 cooperates with doxorubicin to induce apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through p53 or p73 signaling pathways
- PMID: 20174822
- PMCID: PMC11827909
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-010-0817-8
Nutlin-3 cooperates with doxorubicin to induce apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through p53 or p73 signaling pathways
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Nutlin-3 cooperates with doxorubicin to induce apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through p53 or p73 signaling pathways.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021 Nov;147(11):3457-3458. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03543-4. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33528639 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: Despite recent advances in chemotherapeutic agents for Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treatment, the results of chemotherapy remain unsatisfactory. Doxorubicin (DOX) still represents the cornerstone in HCC chemotherapy, but resistance and toxicity to normal cells are major obstacles to successful chemotherapy. Therefore, new active agents in HCC chemotherapy and agents that increase the chemosensitivity of HCC cells to DOX are still urgently required. Nutlin-3 is a small-molecule inhibitor that acts to inhibit murine double minute-2 (MDM2) binding to p53 or p73, and subsequently activates p53- or p73-dependent apoptosis signaling pathway. This study was designed to investigate whether Nutlin-3 alters cell toxicity to HCC cells following DNA damage and to assess the suitability of DOX/Nutlin-3 as a chemotherapeutic combination in HCC chemotherapy.
Methods: Four human HCC cells were analyzed using cell proliferation assay, apoptosis assay, western blotting, co-immunoprecipitation and siRNA experiments. Anti-tumoral effects of Nutlin-3/DOX targeting the p53/MDM2 and p73/MDM2 pathways were evaluated in HCC cell lines.
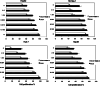
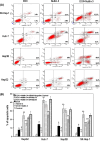
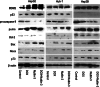
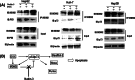
Results: Nutlin-3 enhances the growth inhibition by DOX and potentates the apoptotic effect in all HCC cell lines with different p53 types. Nutlin-3 acts through the disruption of p53-MDM2 binding in HepG2, and the disruption of p73-MDM2 in Huh-7 and Hep3B cell lines with subsequent activation of the apoptotic pathway, which leads to the increase in chemosensitivity to DOX in HCC cells.
Conclusions: Taken together, our findings suggest that Nutlin-3 will be active in the treatment of HCC and offers new prospects for overcoming DOX resistance.
Figures
References
-
- Artandi SE, Attardi LD (2005) Pathways connecting telomeres and p53 in senescence, apoptosis, and cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 331(3):881–890 - PubMed
-
- Bálint E, Bates S, Vousden KH (1999) Mdm2 binds p73 alpha without targeting degradation. Oncogene 18(27):3923–3929 - PubMed
-
- Carr BI (2004) Hepatocellular carcinoma: current management and future trends. Gastroenterology 127:S218–S224 - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Zhang M, Liu LX (2009) The overexpression of multidrug resistance-associated proteins and gankyrin contribute to arsenic trioxide resistance in liver and gastric cancer cells. Oncol Rep 22(1):73–80 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

