Ferritin as a reporter gene for MRI: chronic liver over expression of H-ferritin during dietary iron supplementation and aging
- PMID: 20175142
- PMCID: PMC3558734
- DOI: 10.1002/nbm.1491
Ferritin as a reporter gene for MRI: chronic liver over expression of H-ferritin during dietary iron supplementation and aging
Abstract
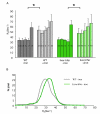
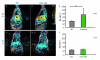
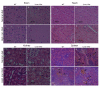
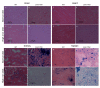
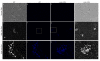
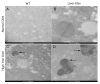
The iron storage protein, ferritin, provides an important endogenous MRI contrast that can be used to determine the level of tissue iron. In recent years the impact of modulating ferritin expression on MRI contrast and relaxation rates was evaluated by several groups, using genetically modified cells, viral gene transfer and transgenic animals. This paper reports the follow-up of transgenic mice that chronically over-expressed the heavy chain of ferritin (h-ferritin) in liver hepatocytes (liver-hfer mice) over a period of 2 years, with the aim of investigating the long-term effects of elevated level of h-ferritin on MR signal and on the well-being of the mice. Analysis revealed that aging liver-hfer mice, exposed to chronic elevated expression of h-ferritin, have increased R(2) values compared to WT. As expected for ferritin, R(2) difference was strongly enhanced at high magnetic field. Histological analysis of these mice did not reveal liver changes with prolonged over expression of ferritin, and no differences could be detected in other organs. Furthermore, dietary iron supplementation significantly affected MRI contrast, without affecting animal wellbeing, for both wildtype and ferritin over expressing transgenic mice. These results suggest the safety of ferritin over-expression, and support the use of h-ferritin as a reporter gene for MRI.
Figures

References
-
- Arredondo M, Nunez MT. Iron and copper metabolism. Mol Aspects Med. 2005;26(4-5):313–327. - PubMed
-
- Chiancone E, Ceci P, Ilari A, Ribacchi F, Stefanini S. Iron and proteins for iron storage and detoxification. Biometals. 2004;17(3):197–202. - PubMed
-
- Siah CW, Trinder D, Olynyk JK. Iron overload. Clin Chim Acta. 2005;358(1-2):24–36. - PubMed
-
- Gottesfeld Z, Neeman M. Ferritin effect on the transverse relaxation of water: NMR microscopy at 9.4 T. Magn Reson Med. 1996;35(4):514–520. - PubMed
-
- Vymazal J, Brooks RA, Bulte JW, Gordon D, Aisen P. Iron uptake by ferritin: NMR relaxometry studies at low iron loads. J Inorg Biochem. 1998;71(3-4):153–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

