[3H]4-(dimethylamino)-N-(4-(4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl) butyl)benzamide: a selective radioligand for dopamine D(3) receptors. II. Quantitative analysis of dopamine D(3) and D(2) receptor density ratio in the caudate-putamen
- PMID: 20175227
- PMCID: PMC3583018
- DOI: 10.1002/syn.20748
[3H]4-(dimethylamino)-N-(4-(4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl) butyl)benzamide: a selective radioligand for dopamine D(3) receptors. II. Quantitative analysis of dopamine D(3) and D(2) receptor density ratio in the caudate-putamen
Abstract
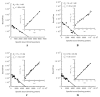
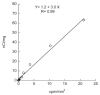
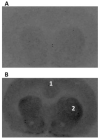
4-(Dimethylamino)-N-(4-(4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)benzamide (WC-10), a N-phenyl piperazine analog, displays high affinity and moderate selectivity for dopamine D(3) receptors versus dopamine D(2) receptors (Chu et al. [2005] Bioorg Med Chem 13:77-87). In this study, WC-10 was radiolabeled with tritium (specific activity = 80 Ci/mmol), and quantitative autoradiography studies were conducted using rhesus monkey and Sprague-Dawley rat brain sections. K(d) values for the binding of [3H]WC-10 to D(3) receptors obtained from quantitative autoradiography with rhesus monkey and rat brain sections are in agreement with K(d) values obtained from cloned human and rat receptors (Xu et al. [2009] Synapse 63:717-728). The D(2) selective antagonist [3H]raclopride binds with 11-fold higher affinity to human HEK D(2L) (K(d) = 1.6 nM) than HEK D(3) (K(d) = 18 nM) receptors; [3H]raclopride binds to rat Sf9 rD(2L) receptors with a K(d) of 6.79 nM, a value that is 4-fold lower than binding to human HEK D(2L) receptors and 2.5-fold higher than binding to rat Sf9 rD(3) receptors. In vitro quantitative autoradiography studies with [3H]WC-10 and [3H]raclopride were conducted on adult rat and rhesus monkey brain sections. A mathematical model for calculating the absolute densities of dopamine D(2) and D(3) receptors based on the in vitro receptor binding data of [3H]WC-10 and [3H]raclopride was developed.
Figures
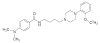


References
-
- Ariano MA, Sibley DR. Dopamine receptor distribution in the rat CNS: Elucidation using anti-peptide antisera directed against D1A and D3 subtypes. Brain Res. 1994;649:95–110. - PubMed
-
- Boundy VA, Luedtke RR, Gallitano AL, Smith JE, Filtz TM, Kallen RG, Molinoff PB. Expression and characterization of the rat D3 dopamine receptor: Pharmacologic properties and development of antibodies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;264:1002–1011. - PubMed
-
- Camacho-Ochoa M, Walker EL, Evans DL, Piercey MF. Rat brain binding sites for pramipexole, a clinically useful D3-preferring dopamine agonist. Neurosci Lett. 1995;196:97–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
