Validation of the ICSD-2 criteria for CSF hypocretin-1 measurements in the diagnosis of narcolepsy in the Danish population
- PMID: 20175400
- PMCID: PMC2817904
- DOI: 10.1093/sleep/33.2.169
Validation of the ICSD-2 criteria for CSF hypocretin-1 measurements in the diagnosis of narcolepsy in the Danish population
Abstract
Study objectives: The International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD-2) criteria for low CSF hypocretin-1 levels (CSF hcrt-1) still need validation as a diagnostic tool for narcolepsy in different populations because inter-assay variability and different definitions of hypocretin deficiency complicate direct comparisons of study results.
Design and participants: Interviews, polysomnography, multiple sleep latency test, HLA-typing, and CSF hcrt-1 measurements in Danish patients with narcolepsy with cataplexy (NC) and narcolepsy without cataplexy (NwC), CSF hcrt-1 measurements in other hypersomnias, neurological and normal controls. Comparisons of hypocretin deficiency and frequency of HLA-DQB1*0602-positivity in the Danish and eligible NC and NwC populations (included via MEDLINE search), by (re)calculation of study results using the ICSD-2 criterion for low CSF hcrt-1 (< 30% of normal mean).
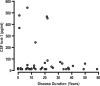
Measurements and results: In Danes, low CSF hcrt-1 was present in 40/46 NC, 3/14 NwC and 0/106 controls (P < 0.0001). Thirty-nine of 41 NC and 4/13 NwC patients were HLA-DQB1*0602-positive (P < 0.01). Hypocretin-deficient NC patients had higher frequency of cataplexy, shorter mean sleep latency, more sleep onset REM periods (P < 0.05) and more awakenings (NS) than did NC patients with normal CSF hcrt-1. Across populations, low CSF hcrt-1 and HLA-DQB1*0602-positivity characterized the majority of NC (80% to 100%, P = 0.53; 80% to 100%, P = 0.11) but a minority of NwC patients (11% to 29%, P = 0.75; 29% to 89%, P = 0.043).
Conclusion: The study provides evidence that hypocretin deficiency causes a more severe NC phenotype. The ICSD-2 criterion for low CSF hcrt-1 (< 30% of normal mean) is valid for diagnosing NC, but not NwC. HLA-typing should precede CSF hcrt-1 measurements because hypocretin deficiency is rare in HLA-DQB1*0602-negative patients.
Figures

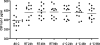
Similar articles
-
The role of cerebrospinal fluid hypocretin measurement in the diagnosis of narcolepsy and other hypersomnias.Arch Neurol. 2002 Oct;59(10):1553-62. doi: 10.1001/archneur.59.10.1553. Arch Neurol. 2002. PMID: 12374492
-
[Comparative analysis of patients with narcolepsy-cataplexy, narcolepsy without cataplexy and idiopathic hypersomnia].Med Clin (Barc). 2007 Mar 17;128(10):361-4. doi: 10.1157/13099970. Med Clin (Barc). 2007. PMID: 17386240 Spanish.
-
A study of the diagnostic utility of HLA typing, CSF hypocretin-1 measurements, and MSLT testing for the diagnosis of narcolepsy in 163 Korean patients with unexplained excessive daytime sleepiness.Sleep. 2006 Nov;29(11):1429-38. doi: 10.1093/sleep/29.11.1429. Sleep. 2006. PMID: 17162989
-
Symptomatic narcolepsy, cataplexy and hypersomnia, and their implications in the hypothalamic hypocretin/orexin system.Sleep Med Rev. 2005 Aug;9(4):269-310. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2005.03.004. Sleep Med Rev. 2005. PMID: 16006155 Review.
-
CSF hypocretin-1 assessment in sleep and neurological disorders.Lancet Neurol. 2008 Jul;7(7):649-62. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70140-6. Lancet Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18565458 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurobiology and sleep disorders in cluster headache.J Headache Pain. 2015;16:562. doi: 10.1186/s10194-015-0562-0. Epub 2015 Aug 20. J Headache Pain. 2015. PMID: 26289164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Operational definitions and algorithms for excessive sleepiness in the general population: implications for DSM-5 nosology.Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;69(1):71-9. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.1240. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22213791 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuated heart rate response is associated with hypocretin deficiency in patients with narcolepsy.Sleep. 2013 Jan 1;36(1):91-8. doi: 10.5665/sleep.2308. Sleep. 2013. PMID: 23288975 Free PMC article.
-
Increased incidence and clinical picture of childhood narcolepsy following the 2009 H1N1 pandemic vaccination campaign in Finland.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33723. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033723. Epub 2012 Mar 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22470463 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Hypocretin-1 (Orexin-A) Level Fluctuates with Season and Correlates with Day Length.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 23;11(3):e0151288. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151288. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27008404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peyron C, Faraco J, Rogers W, et al. A mutation in a case of early onset narcolepsy and a generalized absence of hypocretin peptides in human narcoleptic brains. Nat Med. 2000;6:991–7. - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine. International classification of sleep disorders, 2nd ed.: diagnostic and coding manual. Westchester, IL: American Academy of Sleep Medicine; 2005.
-
- Martinez-Rodriguez JE, Iranzo A, Casamitjana R, Graus F, Santamaria J. [Comparative analysis of patients with narcolepsy-cataplexy, narcolepsy without cataplexy and idiopathic hypersomnia] Med Clin (Barc) 2007;128:361–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

