CT colonography: advanced computer-aided detection scheme utilizing MTANNs for detection of "missed" polyps in a multicenter clinical trial
- PMID: 20175461
- PMCID: PMC2801730
- DOI: 10.1118/1.3263615
CT colonography: advanced computer-aided detection scheme utilizing MTANNs for detection of "missed" polyps in a multicenter clinical trial
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to develop an advanced computer-aided detection (CAD) scheme utilizing massive-training artificial neural networks (MTANNs) to allow detection of "difficult" polyps in CT colonography (CTC) and to evaluate its performance on false-negative (FN) CTC cases that radiologists "missed" in a multicenter clinical trial.
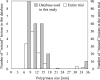
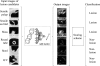
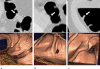
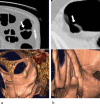
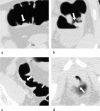
Methods: The authors developed an advanced CAD scheme consisting of an initial polyp-detection scheme for identification of polyp candidates and a mixture of expert MTANNs for substantial reduction in false positives (FPs) while maintaining sensitivity. The initial polyp-detection scheme consisted of (1) colon segmentation based on anatomy-based extraction and colon-based analysis and (2) detection of polyp candidates based on a morphologic analysis on the segmented colon. The mixture of expert MTANNs consisted of (1) supervised enhancement of polyps and suppression of various types of nonpolyps, (2) a scoring scheme for converting output voxels into a score for each polyp candidate, and (3) combining scores from multiple MTANNs by the use of a mixing artificial neural network. For testing the advanced CAD scheme, they created a database containing 24 FN cases with 23 polyps (range of 6-15 mm; average of 8 mm) and a mass (35 mm), which were "missed" by radiologists in CTC in the original trial in which 15 institutions participated.
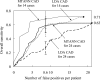
Results: The initial polyp-detection scheme detected 63% (15/24) of the missed polyps with 21.0 (505/24) FPs per patient. The MTANNs removed 76% of the FPs with loss of one true positive; thus, the performance of the advanced CAD scheme was improved to a sensitivity of 58% (14/24) with 8.6 (207/24) FPs per patient, whereas a conventional CAD scheme yielded a sensitivity of 25% at the same FP rate (the difference was statistically significant).
Conclusions: With the advanced MTANN CAD scheme, 58% of the polyps missed by radiologists in the original trial were detected and with a reasonable number of FPs. The results suggest that the use of an advanced MTANN CAD scheme may potentially enhance the detection of "difficult" polyps.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mixture of expert 3D massive-training ANNs for reduction of multiple types of false positives in CAD for detection of polyps in CT colonography.Med Phys. 2008 Feb;35(2):694-703. doi: 10.1118/1.2829870. Med Phys. 2008. PMID: 18383691
-
Massive-training artificial neural network coupled with Laplacian-eigenfunction-based dimensionality reduction for computer-aided detection of polyps in CT colonography.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2010 Nov;29(11):1907-17. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2010.2053213. Epub 2010 Jun 21. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2010. PMID: 20570766 Free PMC article.
-
Massive-training artificial neural network (MTANN) for reduction of false positives in computer-aided detection of polyps: Suppression of rectal tubes.Med Phys. 2006 Oct;33(10):3814-24. doi: 10.1118/1.2349839. Med Phys. 2006. PMID: 17089846
-
CAD techniques, challenges, and controversies in computed tomographic colonography.Abdom Imaging. 2005 Jan-Feb;30(1):26-41. doi: 10.1007/s00261-004-0244-x. Abdom Imaging. 2005. PMID: 15647868 Review.
-
Computer-aided detection for CT colonography: update 2007.Abdom Imaging. 2007 Sep-Oct;32(5):571-81. doi: 10.1007/s00261-007-9293-2. Abdom Imaging. 2007. PMID: 17690932 Review.
Cited by
-
A review of computer-aided diagnosis in thoracic and colonic imaging.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2012 Sep;2(3):163-76. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2012.09.02. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2012. PMID: 23256078 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of deep learning in medical imaging.Radiol Phys Technol. 2017 Sep;10(3):257-273. doi: 10.1007/s12194-017-0406-5. Epub 2017 Jul 8. Radiol Phys Technol. 2017. PMID: 28689314 Review.
-
CT colonography with computer-aided detection: recognizing the causes of false-positive reader results.Radiographics. 2014 Nov-Dec;34(7):1885-905. doi: 10.1148/rg.347130053. Radiographics. 2014. PMID: 25384290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matching 3-D prone and supine CT colonography scans using graphs.IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 2012 Jul;16(4):676-82. doi: 10.1109/TITB.2012.2194297. Epub 2012 Apr 27. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 2012. PMID: 22552585 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative radiology: automated measurement of polyp volume in computed tomography colonography using Hessian matrix-based shape extraction and volume growing.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2015 Oct;5(5):673-84. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2015.10.06. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2015. PMID: 26682137 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society, Cancer Facts & Figures 2008 (American Cancer Society, Atlanta, 2008).
-
- Dachman A. H., Atlas of Virtual Colonoscopy (Springer-Verlag, New York, 2003).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

