Reduced skin homing by functional Treg in vitiligo
- PMID: 20175879
- PMCID: PMC3778930
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2010.00688.x
Reduced skin homing by functional Treg in vitiligo
Erratum in
- Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2010 Jun;23(3):477. Wainwright, Derek J [corrected to Wainwright, Derek A]
Abstract
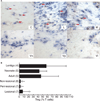
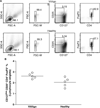
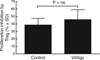
In human vitiligo, cutaneous depigmentation involves cytotoxic activity of autoreactive T cells. It was hypothesized that depigmentation can progress in the absence of regulatory T cells (Treg). The percentage of Treg among skin infiltrating T cells was evaluated by immunoenzymatic double staining for CD3 and FoxP3, revealing drastically reduced numbers of Treg in non-lesional, perilesional and lesional vitiligo skin. Assessment of the circulating Treg pool by FACS analysis of CD4, CD25, CD127 and FoxP3 expression, and mixed lymphocyte reactions in presence and absence of sorted Treg revealed no systemic drop in the abundance or activity of Treg in vitiligo patients. Expression of skin homing receptors CCR4, CCR5, CCR8 and CLA was comparable among circulating vitiligo and control Treg. Treg from either source were equally capable of migrating towards CCR4 ligand and skin homing chemokine CCL22, yet significantly reduced expression of CCL22 in vitiligo skin observed by immunohistochemistry may explain failure of circulating, functional Treg to home to the skin in vitiligo. The paucity of Treg in vitiligo skin is likely crucial for perpetual anti-melanocyte reactivity in progressive disease.
Figures


References
-
- Al-Mutairi N, Al-Doukhi A. Familial coexisting and colocalized psoriasis and vitiligo responding to alefacept. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2009;13:172–175. - PubMed
-
- Baecher-Allen C, Hafler DA. Human regulatory T cells and their role on autoimmune disease. Immunol. Rev. 2006;212:203–216. - PubMed
-
- Bala KK, Moudgil KD. Induction and maintenance of self tolerance: the role of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (Warsz) 2006;54:307–321. - PubMed
-
- Chakraborty NG, Chattopadhyay S, Mehrotra S, Chhabra A, Mukherji B. Regulatory T-cell reponse and tumor vaccine-induced cytotoxic T lymphocytes in human melanoma. Hum. Immunol. 2004;65:794–802. - PubMed
-
- Colantonio L, Iellem A, Sinigaglia F, D’Ambrosio D. Skin-homing CLA+ T cells and regulatory CD25+ T cells represent major subsets of human peripheral blood memory T cells migrating in response to CCL1 / I-309. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002;32:3506–3514. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

